WordPress is well-known for its ease of installation. Under most circumstances, installing WordPress is a very simple process and takes less than five minutes to complete. Many web hosts now offer tools (e.g. Fantastico) to automatically install WordPress for you.
Things to Know Before Installing WordPress
Before you begin the install, there are a few things you need to have and do.
These are:
- Access to your web server (via shell or FTP)
- A text editor
- An FTP Client
- Your web browser of choice
Things You Need to Do to Install WordPress
Begin your installation by:
- Checking to ensure that you and your web host have the minimum requirements to run WordPress.
- Download the latest release of WordPress.
- Unzip the downloaded file to a folder on your hard drive.
- Be prepared with a secure password for your Secret Key
- Print this page out so you have it handy during the installation.
Famous 5-Minute Install
Here's the quick version of the instructions for those who are already comfortable with performing such installations. More detailed instructions follow.
If you are not comfortable with renaming files, Steps 3 and 4 are optional and you can skip them as the install program will create the wp-config.php file for you.
- Download and unzip the WordPress package if you haven't already.
- Create a database for WordPress on your web server, as well as a MySQL user who has all privileges for accessing and modifying it.
- Upload the WordPress files to the desired location on your web server:
- If you want to integrate WordPress into the root of your domain (e.g. http://example.com/), move or upload all contents of the unzipped WordPress directory (excluding the WordPress directory itself) into the root directory of your web server.
- If you want to have your WordPress installation in its own subdirectory on your web site (e.g.http://example.com/blog/), create the blog directory on your server and upload the contents of the unzipped WordPress package to the directory via FTP.
- Note: If your FTP client has an option to convert file names to lower case, make sure it's disabled.
- Run the WordPress installation script by accessing the URL in a web browser. This should be the URL where you uploaded the WordPress files.
- If you installed WordPress in the root directory, you should visit: http://example.com/
- If you installed WordPress in its own subdirectory called blog, for example, you should visit: http://example.com/blog/
That's it! WordPress should now be installed.
Detailed Instructions
Step 1: Download and Extract
Download and unzip the WordPress package from http://wordpress.org/download/.
- If you will be uploading WordPress to a remote web server, download the WordPress package to your computer with a web browser and unzip the package.
- If you will be using FTP, skip to the next step - uploading files is covered later.
- If you have shell access to your web server, and are comfortable using console-based tools, you may wish to download WordPress directly to your web server using wget (or lynx or another console-based web browser) if you want to avoid FTPing:
- wget http://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz
- Then unzip the package using:
tar -xzvf latest.tar.gz
The WordPress package will extract into a folder called wordpress in the same directory that you downloadedlatest.tar.gz.
Step 2: Create the Database and a User
If you are using a hosting provider, you may already have a WordPress database set up for you, or there may be an automated setup solution to do so. Check your hosting provider's support pages or your control panel for clues about whether or not you'll need to create one manually.
If you determine that you'll need to create one manually, follow the instructions for accessing phpMyAdmin on various servers, or follow the instructions for Using cPanel or Using phpMyAdmin below.
If you are installing WordPress on your own web server, follow the Using phpMyAdmin or Using the MySQL Client instructions below to create your WordPress username and database.
If you have only one database and it is already in use, you can install WordPress in it - just make sure to have a distinctive prefix for your tables to avoid over-writing any existing database table.
Using cPanel
If your hosting provider supplies the cPanel hosting control panel, you may follow these simple instructions to create your WordPress username and database. A more complete set of instructions for using cPanel to create the database and user can be found in Using cPanel.
- Log in to your cPanel.
- Click MySQL Database Wizard icon under the Databases section.
- In Step 1. Create a Database enter the database name and click Next Step.
- In Step 2. Create Database Users enter the database user name and the password. Make sure to use a strong password. Click Create User.
- In Step 3. Add User to Database click the All Privileges checkbox and click Next Step.
- In Step 4. Complete the task note the database name and user. Write down the values of hostname, username, databasename, and the password you chose. (Note that hostname will usually be localhost.)
Using Lunarpages.com's custom cPanel (LPCP)
Lunarpages has developed their own version of cPanel.
- Log in to your account.
- Go to Control Panel.
- Click on the button on the left panel labeled 'Go to LPCP'.
- Go to MySQL Manager.
- Add the user name and database name but leave the host name as the default IP number.
- Note the IP address of the database on the right which is different from the default IP number of the host indicated in the above step.
- When modifying the WP-CONFIG.PHP file, use the DB IP number, not 'LOCALHOST'.
- When modifying the WP-CONFIG.PHP file, be sure to use the full name of the database and user name, typically 'accountname_nameyoucreated'.
- Refer to http://wiki.lunarpages.com/Create_and_Delete_MySQL_Users_in_LPCP for more info.
Using phpMyAdmin
If your web server has phpMyAdmin installed, you may follow these instructions to create your WordPress username and database.
Note: These instructions are written for phpMyAdmin 2.6.0; the phpMyAdmin user interface can vary slightly between versions.
- If a database relating to WordPress does not already exist in the Database dropdown on the left, create one:
- Choose a name for your WordPress database ('wordpress' or 'blog' are good), enter it in the Create new database field, and click Create.
- Click the Home icon in the upper left to return to the main page, then click Privileges. If a user relating to WordPress does not already exist in the list of users, create one:
- Click Add a new User.
- Choose a username for WordPress ('wordpress' is good) and enter it in the User name field. (Be sure Use text field: is selected from the dropdown.)
- Choose a difficult-to-guess password (ideally containing a combination of upper- and lower-case letters, numbers, and symbols), and enter it in the Password field. (Be sure Use text field: is selected from the dropdown.) Re-enter the password in the Re-type field.
- Write down the username and password you chose.
- Leave all options under Global privileges at their defaults.
- Click Go.
- Return to the Privileges screen and click the Check privileges icon on the user you've just created for WordPress. In theDatabase-specific privileges section, select the database you've just created for WordPress under the Add privileges to the following database dropdown. The page will refresh with privileges for that database. Click Check All to select all privileges, and click Go.
- On the resulting page, make note of the host name listed after Server: at the top of the page. (This will usually be localhost.)
Using the MySQL Client
You can create MySQL users and databases quickly and easily by running mysql from the shell. The syntax is shown below and the dollar sign is the command prompt:
$ mysql -u adminusername -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 5340 to server version: 3.23.54
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the buffer.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE databasename;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON databasename.* TO "wordpressusername"@"hostname"
-> IDENTIFIED BY "password";
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> EXIT
Bye
$
The example shows:
- that root is also the adminusername. It is a safer practice to choose a so-called "mortal" account as your mysql admin, so that you are not entering the command "mysql" as the root user on your system. (Any time you can avoid doing work as root you decrease your chance of being exploited). The name you use depends on the name you assigned as the database administrator using mysqladmin.
- wordpress or blog are good values for databasename.
- wordpress is a good value for wordpressusername but you should realize that, since it is used here, the entire world will know it too.
- hostname will usually be localhost. If you don't know what this value should be, check with your system administrator if you are not the admin for your Wordpress host. If you are the system admin, consider using a non-root account to administer your database.
- password should be a difficult-to-guess password, ideally containing a combination of upper- and lower-case letters, numbers, and symbols. One good way of avoiding the use of a word found in a dictionary is to use the first letter of each word in a phrase that you find easy to remember.
If you need to write these values somewhere, avoid writing them in the system that contains the things protected by them. You need to remember the value used for databasename, wordpressusername, hostname, and password. Of course, since they are already in (or will be shortly) your wp-config.php file, there is no need to put them somewhere else, too.
Using DirectAdmin
a. Regular "User" of a single-site webhosting account logs in normally. Then click "MySQL Management." (If this is not readily visible, perhaps your host needs to modify your "package" to activate MySQL.) Then follow part "c" below.
b. "Reseller" accounts or "Admin" accounts may need to click "User Level." They also must first log-in as "Reseller" if the relevant domain is a Reseller's primary domain... or log-in as a "User" if the domain is not a Reseller's primary domain. If a Reseller's primary domain, then when logged-in as Reseller, you simply click "User Level." However if the relevant domain is not the Reseller's primary domain, then you must log-in as the relevant User. Then click "MySQL Management." (If not readily visible, perhaps you need to return to the Reseller or Admin level, and modify the "Manage user package" or "Manage Reseller package" to enable MySQL.)
c. In "MySQL Management," click on the small words: "Create new database." Here you are asked to submit two suffixes for the database and its username. For maximum security, use two different sets of 4-6 random characters. Then the password field has a "Random" button that generates an 8-character password. You may also add more characters to the password for maximum security. "Create." The next screen will summarize the database, username, password and hostname. Be sure to copy and paste these into a text file for future reference.
Step 3: Set up wp-config.php
You can either create and edit the wp-config.php file yourself, or you can skip this step and let WordPress try to do this itselfwhen you run the installation script (step 5) (you'll still need to tell WordPress your database information).
(For more extensive details, and step by step instructions for creating the configuration file and your secret key for password security, please see Editing wp-config.php.)
Return to where you extracted the WordPress package in Step 1, rename the file wp-config-sample.php to wp-config.php, and open it in a text editor.
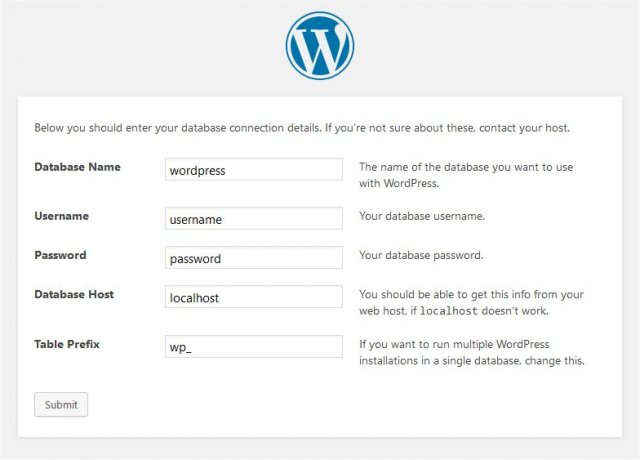
Enter your database information under the section labeled
// ** MySQL settings - You can get this info from your web host ** //
- DB_NAME
- The name of the database you created for WordPress in Step 2 .
- DB_USER
- The username you created for WordPress in Step 2.
- DB_PASSWORD
- The password you chose for the WordPress username in Step 2.
- DB_HOST
- The hostname you determined in Step 2 (usually localhost, but not always; see some possible DB_HOST values). If a port, socket, or pipe is necessary, append a colon (:) and then the relevant information to the hostname.
- DB_CHARSET
- The database character set, normally should not be changed (see Editing wp-config.php).
- DB_COLLATE
- The database collation should normally be left blank (see Editing wp-config.php).
Enter your secret key values under the section labeled
* Authentication Unique Keys.
Save the wp-config.php file.
For information on enabling SSL in WordPress 2.6, see SSL and Cookies in WordPress 2.6.
Step 4: Upload the files
Now you will need to decide where on your domain you'd like your WordPress-powered site to appear:
- In the root directory of your web site. (For example, http://example.com/)
- In a subdirectory of your web site. (For example, http://example.com/blog/)
Note: The location of your root web directory in the filesystem on your web server will vary across hosting providers and operating systems. Check with your hosting provider or system administrator if you do not know where this is.
In the Root Directory
- If you need to upload your files to your web server, use an FTP client to upload all the contents of the wordpress directory (but not the directory itself) into the root directory of your web site.
- If your files are already on your web server, and you are using shell access to install WordPress, move all of the contents of thewordpress directory (but not the directory itself) into the root directory of your web site.
In a Subdirectory
- If you need to upload your files to your web server, rename the wordpress directory to your desired name, then use an FTP client to upload the directory to your desired location within the root directory of your web site.
- If your files are already on your web server, and you are using shell access to install WordPress, move the wordpress directory to your desired location within the root directory of your web site, and rename the directory to your desired name.
Note: If your FTP client has an option to convert file names to lower case, make sure it's disabled.
Step 5: Run the Install Script
Point a web browser to start the installation script.
- If you placed the WordPress files in the root directory, you should visit: http://example.com/wp-admin/install.php
- If you placed the WordPress files in a subdirectory called blog, for example, you should visit:http://example.com/blog/wp-admin/install.php
Setup configuration file
If WordPress can't find the wp-config.php file, it will tell you and offer to try to create and edit the file itself. (You can do also do this directly by loading wp-admin/setup-config.php in your web browser.) WordPress will ask you the database details and write them to a new wp-config.php file. If this works, you can go ahead with the installation; otherwise, go back and create, edit, and upload the wp-config.php file yourself (step 3).
Finishing installation
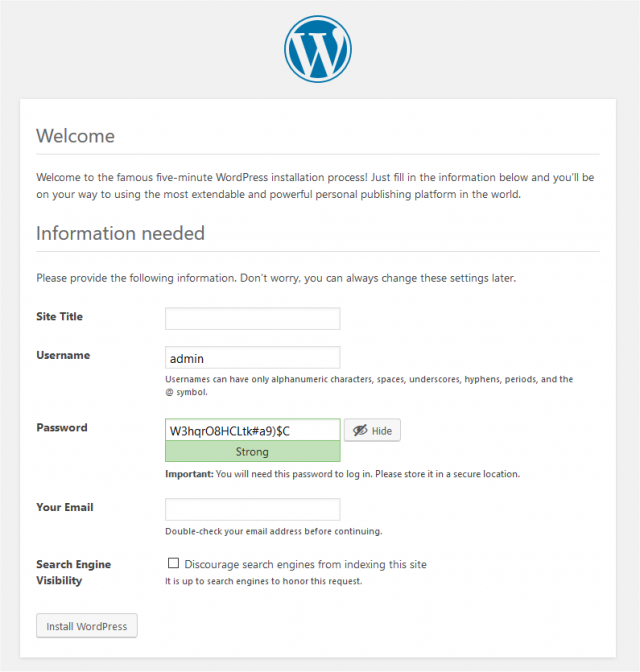
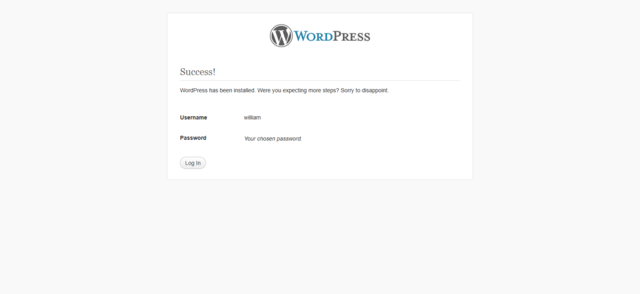
The following screenshots show how the installation progresses. Notice in Entering the details screen, you enter your site title, your desired user name, your choice of a password (twice) and your e-mail address. Also displayed is a check-box asking if you would like your blog to appear in search engines like Google and Technorati. Leave the box checked if you would like your blog to be visible to everyone, including search engines, and uncheck the box if you want to block search engines, but allow normal visitors. Note all this information can be changed later in your Administration Panels.
Install Script Troubleshooting
- If you get an error about the database when you run the install script:
Common Installation Problems
The following are some of the most common installation problems. For more information and troubleshooting for problems with your WordPress installation, check out FAQ Installation and FAQ Troubleshooting.
I see a directory listing rather than a web page.
The web server needs to be told to view index.php by default. In Apache, use the DirectoryIndex index.php directive. The simplest option is to create a file named .htaccess in the installed directory and place the directive there. Another option is to add the directive to the web server's configuration files.
I see lots of Headers already sent errors. How do I fix this?
You probably introduced a syntax error in editing wp-config.php.
- Download wp-config.php (if you don't have shell access).
- Open it in a text editor.
- Check that the first line contains nothing but <?php, and that there is no text before it (not even whitespace).
- Check that the last line contains nothing but ?>, and that there is no text after it (not even whitespace).
- If your text editor saves as Unicode, make sure it adds no byte order mark (BOM). Most Unicode-enabled text editors do not inform the user whether it adds a BOM to files; if so, try using a different text editor.
- Save the file, upload it again if necessary, and reload the page in your browser.
My page comes out gibberish. When I look at the source I see a lot of "<?php ?>" tags.
If the <?php ?> tags are being sent to the browser, it means your PHP is not working properly. All PHP code is supposed to be executed before the server sends the resulting HTML to your web browser. (That's why it's called a preprocessor.) Make sure your web server meets the requirements to run WordPress, that PHP is installed and configured properly, or contact your hosting provider or system administrator for assistance.
I keep getting an Error connecting to database message but I'm sure my configuration is correct.
Try resetting your MySQL password manually. If you have access to MySQL via shell, try issuing:
SET PASSWORD FOR 'wordpressusername'@'hostname' = OLD_PASSWORD('password');
If you are using a version of MySQL prior to 4.1, use PASSWORD instead of OLD_PASSWORD. If you do not have shell access, you should be able to simply enter the above into an SQL query in phpMyAdmin. Failing that, you may need to use your host's control panel to reset the password for your database user.
My image/MP3 uploads aren't working.
If you use the Rich Text Editor on a blog that's installed in a subdirectory, and drag a newly uploaded image into the editor field, the image may vanish a couple seconds later. This is due to a problem with TinyMCE (the rich text editor) not getting enough information during the drag operation to construct the path to the image or other file correctly. The solution is to NOT drag uploaded images into the editor. Instead, click and hold on the image and select "Send to Editor."
Automated Installation
Although WordPress is very easy to install, you can use one of the one-click autoinstallers typically available from hosting companies. Four of those autoinstallers, (mt) Media Temple 1-Click Tool, Fantastico, Installatron 1-Click Installer, and Softaculous are described here.
(mt) Media Temple 1-Click Tool
- Log into your AccountCenter at https://ac.mediatemple.net and choose the primary domain of your (gs) Grid-Service.
- Click on "1-Click Applications", then click "Add New Application".
- Click the "Start" button for WordPress.
4. Input various setup details and click "Install".
5. Then click on "Finish" and your Wordpress installation is complete!
5. Then click on "Finish" and your Wordpress installation is complete!
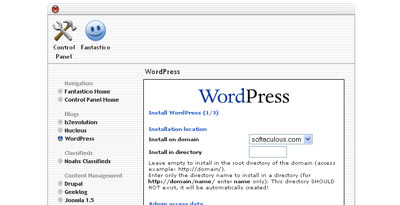
Fantastico
- Login to your cPanel account and click on the Fantastico (or Fantastico Deluxe) option
- Once you enter Fantastico on the left hand side there is a 'Blogs' Category under which WordPress is there. Click on it.
- Click on the 'New Installation' Link in the WordPress Overview
- Fill in the various details and Submit.
- That's it you are done!
Installatron 1-Click Installer
Installatron is a one-click web application installer that enables WordPress and other top web applications to be instantly installed and effortlessly managed. Get WordPress up and running on your website in seconds and discover just how easy Installatron makes managing web applications. WordPress installations managed by Installatron can updated (manually or automated), cloned, backed up and restored, edited to change installation parameters, and more.
Many web hosting providers include Installatron through their web hosting control panel. If Installatron is not available from your provider, you can use Installatron directly from Installatron.com.
To install WordPress through your web hosting provider's control panel:
- Login to your web host's control panel, navigate to "Installatron", click "WordPress", and choose the "Install this application" option.
- Change any of the install prompts to customize the install. For example, you can choose a different language for WordPress.
- Click the "Install" button to begin the installation process. You will be redirect to a progress page where you can watch as WordPress is installed within a few seconds to your website.
To install WordPress using Installatron.com:
- Navigate to WordPress @ Installatron and choose the "Install this application" option.
- Enter your hosting account's FTP or SSH account information, and then enter MySQL database information for a created database. For increased security, create a separate FTP account and MySQL database for your WordPress installation.
- Change any of the install prompts to customize the install. For example, you can choose a different language for WordPress.
- Click the "Install" button to begin the installation process. You will be redirect to a progress page where you can watch as WordPress is installed within a few seconds to your website.
If you experience any problems or want to share your experience using WordPress and Installatron together, email Installatron at: feedback@installatron.com
Softaculous
- Login to your host and look for Software/Services
- In Softaculous there is a 'Blogs' Category. Collapse the category and WordPress will be there. Click on it.
- You will see an 'Install' TAB. Click it.
- Fill in the various details and Submit.
- That's it, you are done!
Installation Instructions in Other Languages
For installation instructions in other languages, see WordPress in Your Language.
Installing Multiple Blogs
Detailed information about Installing Multiple Blogs is available.
Installing WordPress on your own Computer
Local Installation Instructions
Use these instruction for setting up a local server environment for testing and development.
- DesktopServer Limited: Free Windows/Macintosh server, creates multiple virtual servers with fictitious top level domains (i.e. www.example.dev) specifically for working on multiple WordPress projects.
- Mac App Store 1-click install for WordPress Installs a free, self-contained all-in-one bundle of WordPress and everything it needs to run: MySQL, Apache and PHP
- Installing WordPress Locally on Your Mac With MAMP
- User:Beltranrubo/BitNami Free all-in-one installers for OS X, Windows and Linux. There are also available installers for WordPress Multisite User:Beltranrubo/BitNami_Multisite using different domains or subdomains.
- Instant WordPress is a free, standalone, portable WordPress development environment for Windows that will run from a USB key.
Software Appliance - Ready-to-Use
You may find that using a pre-integrated software appliance is a great way to get up and running with WordPress, especially in combination with virtual machine software (e.g., VMWare, VirtualBox, Xen HVM, KVM).
A software appliance allows users to altogether skip manual installation of WordPress and its dependencies, and instead deploy a self-contained system that requires little to no setup, in just a couple of minutes.
- TurnKey WordPress Appliance: a free Ubuntu-based appliance that just works. It bundles a collection of popular WordPress plugins and features a small footprint, automatic security updates, SSL support and a Web administration interface.
- BitNami WordPress Appliance: free WordPress appliances based on Ubuntu or Open Suse. Native installer and Cloud images also available. There are also virtual machines for WordPress Multisite already configured.
- UShareSoft WordPress Appliance: free WordPress appliance for many of the major virtualization and cloud platforms (Cloud.com, Xen, VMware, OVF, Abiquo)
Easy 5 Minute WordPress Installation on Windows
Download, install, and configure WordPress with the Microsoft Web Platform Installer (Web PI). Installation is very easy and takes on average about 5 minutes to complete. For other Windows installers, check this section
- Step 1. Things you need to know before starting.
- These steps will work on Windows versions which include IIS, such as Windows XP professional, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows Server.
- You must be able to install programs on your machine (i.e. have administrator rights).
- Once Web PI is installed, neither XAMPP nor any other web server will be able to use localhost to host a web site locally on your machine.
- Step 2. Navigate to the WordPress Installation Page
- Choose the "Install" button.
- If you have Web PI already installed, it will automatically be launched and you can skip to the next step.
- If you do not have the Web Platform Installer, you will be prompted to install it.
- Web PI is a tool from Microsoft that downloads and installs the latest components you need to develop or host Web applications on Windows. Everything in the tool is free. Web PI will install and configure IIS, PHP, MySQL and anything else you may need.
- Step 3. Choose to Install WordPress
- When Web PI launches, you will see an information page for WordPress. Start installing WordPress by pressing the "Install" button in the lower right hand corner.
- Step 4. Installation of WordPress and its requirements
- Finding Dependencies: Web PI will determine the minimum set of components and modules you need on your machine to run WordPress. It will only install what you’re missing. For example, PHP will be installed and configured to run WordPress.
- Configure the Database: After accepting the terms, if you need to install MySQL, you will be asked to create a password for the root account database account. Keep this password safe. WordPress will ask for this information later.
- Choose the site: Choose a site to install WordPress to. You may install to an existing Web site in IIS or create a new site. Use the default setting if you do not have advanced configuration needs.
- WordPress Setup: WordPress will need answers to a few specific questions such as the username (in the case of a new MySQL install is root) and password for your MySQL database to complete the install.
- Step 5. Completion
- Once you enter the WordPress setup information, Web PI will finish the installation.
- Click, Launch in Browser and WordPress will launch.
Alternatively, the BitNami WordPress installer is a free, self-contained native installer for WordPress that includes Apache, MySQL and PHP so it works out of the box.