Android is an open source and Linux-based operating system for mobile
devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. Android was developed
by the Open Handset Alliance, led by Google, and other companies.
This tutorial will teach you basic Android programming and will also take you through some advance concepts related to Android application development.
 Android is an open source and Linux-based Operating System for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. Android was developed by the Open Handset Alliance, led by Google, and other companies.
Android is an open source and Linux-based Operating System for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. Android was developed by the Open Handset Alliance, led by Google, and other companies.
Android offers a unified approach to application development for mobile devices which means developers need only develop for Android, and their applications should be able to run on different devices powered by Android.
The first beta version of the Android Software Development Kit (SDK) was released by Google in 2007 where as the first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released in September 2008.
On June 27, 2012, at the Google I/O conference, Google announced the next Android version, 4.1 Jelly Bean. Jelly Bean is an incremental update, with the primary aim of improving the user interface, both in terms of functionality and performance.
The source code for Android is available under free and open source software licenses. Google publishes most of the code under the Apache License version 2.0 and the rest, Linux kernel changes, under the GNU General Public License version 2.

Once developed, Android applications can be packaged easily and sold out either through a store such as Google Play,SlideME,Opera Mobile Store,Mobango,F-droid and the Amazon Appstore.
Android powers hundreds of millions of mobile devices in more than 190 countries around the world. It's the largest installed base of any mobile platform and growing fast. Every day more than 1 million new Android devices are activated worldwide.
This tutorial has been written with an aim to teach you how to develop and package Android application. We will start from environment setup for Android application programming and then drill down to look into various aspects of Android applications.


If you are running Windows and installed the JDK in C:\jdk1.6.0_15, you would have to put the following line in your C:\autoexec.bat file.
On Linux, if the SDK is installed in /usr/local/jdk1.6.0_15 and you use the C shell, you would put the following code into your .cshrc file.
The Dalvik VM makes use of Linux core features like memory management and multi-threading, which is intrinsic in the Java language. The Dalvik VM enables every Android application to run in its own process, with its own instance of the Dalvik virtual machine.
The Android runtime also provides a set of core libraries which enable Android application developers to write Android applications using standard Java programming language.
The Android framework includes the following key services −
There are following four main components that can be used within an Android application:
An activity is implemented as a subclass of Activity class as follows −
A service is implemented as a subclass of Service class as follows −
A broadcast receiver is implemented as a subclass of BroadcastReceiver class and each message is broadcaster as an Intent object.
A content provider is implemented as a subclass of ContentProvider class and must implement a standard set of APIs that enable other applications to perform transactions.
So let us proceed to write a simple Android Application which will print "Hello World!".
 Next, follow the instructions provided and keep all other entries as
default till the final step. Once your project is created successfully,
you will have following project screen −
Next, follow the instructions provided and keep all other entries as
default till the final step. Once your project is created successfully,
you will have following project screen −


Following section will give a brief overview few of the important application files.
The <activity> tag is used to specify an activity and android:name attribute specifies the fully qualified class name of the Activity subclass and the android:label attributes specifies a string to use as the label for the activity. You can specify multiple activities using <activity> tags.
The action for the intent filter is named android.intent.action.MAIN to indicate that this activity serves as the entry point for the application. The category for the intent-filter is named android.intent.category.LAUNCHER to indicate that the application can be launched from the device's launcher icon.
The @string refers to the strings.xml file explained below. Hence, @string/app_name refers to the app_name string defined in the strings.xml file, which is "HelloWorld". Similar way, other strings get populated in the application.
Following is the list of tags which you will use in your manifest file to specify different Android application components:
 icon from the tool bar. Eclipse installs the app on your AVD and starts
it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application, it will
display following Emulator window −
icon from the tool bar. Eclipse installs the app on your AVD and starts
it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application, it will
display following Emulator window −
 Congratulations!!! you have developed your first Android Application
and now just keep following rest of the tutorial step by step to become a
great Android Developer. All the very best.
Congratulations!!! you have developed your first Android Application
and now just keep following rest of the tutorial step by step to become a
great Android Developer. All the very best.
 The Activity class defines the following call backs i.e. events. You
don't need to implement all the callbacks methods. However, it's
important that you understand each one and implement those that ensure
your app behaves the way users expect.
The Activity class defines the following call backs i.e. events. You
don't need to implement all the callbacks methods. However, it's
important that you understand each one and implement those that ensure
your app behaves the way users expect.
Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/com.example.helloworld/MainActivity.java. This file includes each of the fundamental life cycle methods. The Log.d() method has been used to generate log messages:
Let's try to run our modified Hello World! application we just modified. I assume you had created your AVD while doing environment setup. To run the app from Eclipse, open one of your project's activity files and click Run icon from the toolbar. Eclipse installs the app on your AVD and starts
it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it will
display Emulator window and you should see following log messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:
icon from the toolbar. Eclipse installs the app on your AVD and starts
it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it will
display Emulator window and you should see following log messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:
 Let us try to click Red button
Let us try to click Red button  on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:
on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:
 on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:
on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:
 on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE and this completes the Activity Life Cycle for an Android Application.
on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE and this completes the Activity Life Cycle for an Android Application.
A service has life cycle callback methods that you can implement to
monitor changes in the service's state and you can perform work at the
appropriate stage. The following diagram on the left shows the life
cycle when the service is created with startService() and the diagram on
the right shows the life cycle when the service is created with
bindService(): (image courtesy : android.com )
 To create an service, you create a Java class that extends the Service base class or one of its existing subclasses. The Service
base class defines various callback methods and the most important are
given below. You don't need to implement all the callbacks methods.
However, it's important that you understand each one and implement those
that ensure your app behaves the way users expect.
To create an service, you create a Java class that extends the Service base class or one of its existing subclasses. The Service
base class defines various callback methods and the most important are
given below. You don't need to implement all the callbacks methods.
However, it's important that you understand each one and implement those
that ensure your app behaves the way users expect.
The following skeleton service demonstrates each of the life cycle methods −
Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/com.example.My Application/MainActivity.java. This file can include each of the fundamental life cycle methods. We have added startService() and stopService() methods to start and stop the service.
 icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window −
icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window −
 Now to start your service, let's click on Start Service button, this will start the service and as per our programming in onStartCommand() method, a message Service Started will appear on the bottom of the the simulator as follows −
Now to start your service, let's click on Start Service button, this will start the service and as per our programming in onStartCommand() method, a message Service Started will appear on the bottom of the the simulator as follows −
 To stop the service, you can click the Stop Service button.
To stop the service, you can click the Stop Service button.

There are several system generated events defined as final static fields in the Intent class. The following table lists a few important system events.
Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/com.example.My Application/MainActivity.java. This file can include each of the fundamental life cycle methods. We have added broadcastIntent() method to broadcast a custom intent.
 icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window −
icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window −
 Now to broadcast our custom intent, let's click on Broadcast Intent button, this will broadcast our custom intent "com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"
which will be intercepted by our registered BroadcastReceiver i.e.
MyReceiver and as per our implemented logic a toast will appear on the
bottom of the the simulator as follows −
Now to broadcast our custom intent, let's click on Broadcast Intent button, this will broadcast our custom intent "com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"
which will be intercepted by our registered BroadcastReceiver i.e.
MyReceiver and as per our implemented logic a toast will appear on the
bottom of the the simulator as follows −
 You can try implementing other BroadcastReceiver to intercept system
generated intents like system boot up, date changed, low battery etc.
You can try implementing other BroadcastReceiver to intercept system
generated intents like system boot up, date changed, low battery etc.

A content provider is implemented as a subclass of ContentProvider class and must implement a standard set of APIs that enable other applications to perform transactions.

Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/com.example.My Application/MainActivity.java. This file can include each of the fundamental life cycle methods. We have added two new methods onClickAddName() and onClickRetrieveStudents() to handle user interaction with the application.
 icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window, be patience because it may
take sometime based on your computer speed:
icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window, be patience because it may
take sometime based on your computer speed:
 Now let's enter student Name and Grade and finally click on Add Name
button, this will add student record in the database and will flash a
message at the bottom showing ContentProvider URI along with record
number added in the database. This operation makes use of our insert() method. Let's repeat this process to add few more students in the database of our content provider.
Now let's enter student Name and Grade and finally click on Add Name
button, this will add student record in the database and will flash a
message at the bottom showing ContentProvider URI along with record
number added in the database. This operation makes use of our insert() method. Let's repeat this process to add few more students in the database of our content provider.
 Once you are done with adding records in the database, now its time
to ask ContentProvider to give us those records back, so let's click Retrieve Students button which will fetch and display all the records one by one which is as per our the implementation of our query() method.
Once you are done with adding records in the database, now its time
to ask ContentProvider to give us those records back, so let's click Retrieve Students button which will fetch and display all the records one by one which is as per our the implementation of our query() method.
You can write activities against update and delete operations by providing callback functions in MainActivity.java file and then modify user interface to have buttons for update and deleted operations in the same way as we have done for add and read operations.
This way you can use existing Content Provider like Address Book or you can use Content Provider concept in developing nice database oriented applications where you can perform all sort of database operations like read, write, update and delete as explained above in the example.
Prior to fragment introduction, we had a limitation because we can show only a single activity on the screen at one given point in time. So we were not able to divide device screen and control different parts separately. But with the introduction of fragment we got more flexibility and removed the limitation of having a single activity on the screen at a time. Now we can have a single activity but each activity can comprise of multiple fragments which will have their own layout, events and complete life cycle.
Following is a typical example of how two UI modules defined by fragments can be combined into one activity for a tablet design, but separated for a handset design.
 The application can embed two fragments in Activity A, when running
on a tablet-sized device. However, on a handset-sized screen, there's
not enough room for both fragments, so Activity A includes only the
fragment for the list of articles, and when the user selects an article,
it starts Activity B, which includes the second fragment to read the
article.
The application can embed two fragments in Activity A, when running
on a tablet-sized device. However, on a handset-sized screen, there's
not enough room for both fragments, so Activity A includes only the
fragment for the list of articles, and when the user selects an article,
it starts Activity B, which includes the second fragment to read the
article.

Some examples of action/data pairs are −
You can check detail on Intent Filters in below section to understand how do we use categories to choose appropriate activity corresponding to an Intent.
The component name is set by setComponent(), setClass(), or setClassName() and read by getComponent().

 These intents designate the target component by its name and they are
typically used for application-internal messages - such as an activity
starting a subordinate service or launching a sister activity. For
example −
These intents designate the target component by its name and they are
typically used for application-internal messages - such as an activity
starting a subordinate service or launching a sister activity. For
example −
 The target component which receives the intent can use the getExtras() method to get the extra data sent by the source component. For example −
The target component which receives the intent can use the getExtras() method to get the extra data sent by the source component. For example −
Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/com.example.My Application/MainActivity.java.
 icon from the toolbar.Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it
will display following Emulator window −
icon from the toolbar.Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it
will display following Emulator window −
 Now click on Start Browser button, which will start a browser configured and display http://www.example.com as shown below −
Now click on Start Browser button, which will start a browser configured and display http://www.example.com as shown below −
 Similar way you can launch phone interface using Start Phone button, which will allow you to dial already given phone number.
Similar way you can launch phone interface using Start Phone button, which will allow you to dial already given phone number.
Following is an example of a part of AndroidManifest.xml file to specify an activity com.example.My Application.CustomActivity which can be invoked by either of the two mentioned actions, one category, and one data −
The <data> element specifies the data type expected by the activity to be called and for above example our custom activity expects the data to start with the "http://"
There may be a situation that an intent can pass through the filters of more than one activity or service, the user may be asked which component to activate. An exception is raised if no target can be found.
There are following test Android checks before invoking an activity −
Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/MainActivity.java.
 icon from the toolbar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it
will display following Emulator window −
icon from the toolbar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it
will display following Emulator window −
 Now let's start with first button "Start Browser with VIEW Action".
Here we have defined our custom activity with a filter
"android.intent.action.VIEW", and there is already one default activity
against VIEW action defined by Android which is launching web browser,
So android displays following two options to select the activity you
want to launch.
Now let's start with first button "Start Browser with VIEW Action".
Here we have defined our custom activity with a filter
"android.intent.action.VIEW", and there is already one default activity
against VIEW action defined by Android which is launching web browser,
So android displays following two options to select the activity you
want to launch.
 Now if you select Browser, then Android will launch web browser and
open example.com website but if you select IndentDemo option then
Android will launch CustomActivity which does nothing but just capture
passed data and displays in a text view as follows −
Now if you select Browser, then Android will launch web browser and
open example.com website but if you select IndentDemo option then
Android will launch CustomActivity which does nothing but just capture
passed data and displays in a text view as follows −
 Now go back using back button and click on "Start Browser with LAUNCH
Action" button, here Android applies filter to choose define activity
and it simply launch your custom activity
Now go back using back button and click on "Start Browser with LAUNCH
Action" button, here Android applies filter to choose define activity
and it simply launch your custom activity
Again, go back using back button and click on "Exception Condition" button, here Android tries to find out a valid filter for the given intent but it does not find a valid activity defined because this time we have used data as https instead of http though we are giving a correct action, so Android raises an exception and shows following screen −
The ViewGroup is a subclass of View and provides invisible container that hold other Views or other ViewGroups and define their layout properties.
At third level we have different layouts which are subclasses of ViewGroup class and a typical layout defines the visual structure for an Android user interface and can be created either at run time using View/ViewGroup objects or you can declare your layout using simple XML file main_layout.xml which is located in the res/layout folder of your project.

Here width and height are the dimension of the layout/view which can
be specified in terms of dp (Density-independent Pixels), sp (
Scale-independent Pixels), pt ( Points which is 1/72 of an inch), px(
Pixels), mm ( Millimeters) and finally in (inches).
You can specify width and height with exact measurements but more often, you will use one of these constants to set the width or height −

You define your layout in an XML file which offers a human-readable structure for the layout, similar to HTML. For example, a simple vertical layout with a text view and a button looks like this −
As explained in previous chapter, a view object may have a unique ID assigned to it which will identify the View uniquely within the tree. The syntax for an ID, inside an XML tag is −
This tutorial will teach you basic Android programming and will also take you through some advance concepts related to Android application development.
Audience
This tutorial has been prepared for the beginners to help them understand basic Android programming. After completing this tutorial you will find yourself at a moderate level of expertise in Android programming from where you can take yourself to next levels.Prerequisites
Android programming is based on Java programming language so if you have basic understanding on Java programming then it will be a fun to learn Android application development.What is Android?
 Android is an open source and Linux-based Operating System for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. Android was developed by the Open Handset Alliance, led by Google, and other companies.
Android is an open source and Linux-based Operating System for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. Android was developed by the Open Handset Alliance, led by Google, and other companies.Android offers a unified approach to application development for mobile devices which means developers need only develop for Android, and their applications should be able to run on different devices powered by Android.
The first beta version of the Android Software Development Kit (SDK) was released by Google in 2007 where as the first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released in September 2008.
On June 27, 2012, at the Google I/O conference, Google announced the next Android version, 4.1 Jelly Bean. Jelly Bean is an incremental update, with the primary aim of improving the user interface, both in terms of functionality and performance.
The source code for Android is available under free and open source software licenses. Google publishes most of the code under the Apache License version 2.0 and the rest, Linux kernel changes, under the GNU General Public License version 2.
Why Android ?

Features of Android
Android is a powerful operating system competing with Apple 4GS and supports great features. Few of them are listed below:| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Beautiful UI | Android OS basic screen provides a beautiful and intuitive user interface. |
| Connectivity | GSM/EDGE, IDEN, CDMA, EV-DO, UMTS, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, LTE, NFC and WiMAX. |
| Storage | SQLite, a lightweight relational database, is used for data storage purposes. |
| Media support | H.263, H.264, MPEG-4 SP, AMR, AMR-WB, AAC, HE-AAC, AAC 5.1, MP3, MIDI, Ogg Vorbis, WAV, JPEG, PNG, GIF, and BMP |
| Messaging | SMS and MMS |
| Web browser | Based on the open-source WebKit layout engine, coupled with Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine supporting HTML5 and CSS3. |
| Multi-touch | Android has native support for multi-touch which was initially made available in handsets such as the HTC Hero. |
| Multi-tasking | User can jump from one task to another and same time various application can run simultaneously. |
| Resizable widgets | Widgets are resizable, so users can expand them to show more content or shrink them to save space |
| Multi-Language | Supports single direction and bi-directional text. |
| GCM | Google Cloud Messaging (GCM) is a service that lets developers send short message data to their users on Android devices, without needing a proprietary sync solution. |
| Wi-Fi Direct | A technology that lets apps discover and pair directly, over a high-bandwidth peer-to-peer connection. |
| Android Beam | A popular NFC-based technology that lets users instantly share, just by touching two NFC-enabled phones together. |
Android Applications
Android applications are usually developed in the Java language using the Android Software Development Kit.Once developed, Android applications can be packaged easily and sold out either through a store such as Google Play,SlideME,Opera Mobile Store,Mobango,F-droid and the Amazon Appstore.
Android powers hundreds of millions of mobile devices in more than 190 countries around the world. It's the largest installed base of any mobile platform and growing fast. Every day more than 1 million new Android devices are activated worldwide.
This tutorial has been written with an aim to teach you how to develop and package Android application. We will start from environment setup for Android application programming and then drill down to look into various aspects of Android applications.
Categories of Android applications
There are many android applications in the market. The top categories are:
History of Android
The code names of android ranges from A to L currently, such as Aestro, Blender, Cupcake, Donut, Eclair, Froyo, Gingerbread, Honeycomb, Ice Cream Sandwitch, Jelly Bean, KitKat and Lollipop. Let's understand the android history in a sequence.
What is API level?
API Level is an integer value that uniquely identifies the framework API revision offered by a version of the Android platform.
| Platform Version | API Level | VERSION_CODE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android 5.1 | 22 | LOLLIPOP_MR1 | |
| Android 5.0 | 21 | LOLLIPOP | |
| Android 4.4W | 20 | KITKAT_WATCH | KitKat for Wearables Only |
| Android 4.4 | 19 | KITKAT | |
| Android 4.3 | 18 | JELLY_BEAN_MR2 | |
| Android 4.2, 4.2.2 | 17 | JELLY_BEAN_MR1 | |
| Android 4.1, 4.1.1 | 16 | JELLY_BEAN | |
| Android 4.0.3, 4.0.4 | 15 | ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH_MR1 | |
| Android 4.0, 4.0.1, 4.0.2 | 14 | ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH | |
| Android 3.2 | 13 | HONEYCOMB_MR2 | |
| Android 3.1.x | 12 | HONEYCOMB_MR1 | |
| Android 3.0.x | 11 | HONEYCOMB | |
| Android 2.3.4 Android 2.3.3 |
10 | GINGERBREAD_MR1 | |
| Android 2.3.2 Android 2.3.1 Android 2.3 |
9 | GINGERBREAD | |
| Android 2.2.x | 8 | FROYO | |
| Android 2.1.x | 7 | ECLAIR_MR1 | |
| Android 2.0.1 | 6 | ECLAIR_0_1 | |
| Android 2.0 | 5 | ECLAIR | |
| Android 1.6 | 4 | DONUT | |
| Android 1.5 | 3 | CUPCAKE | |
| Android 1.1 | 2 | BASE_1_1 | |
| Android 1.0 | 1 | BASE |
Android - Environment Setup
You will be glad to know that you can start your Android application development on either of the following operating systems −- Microsoft Windows XP or later version.
- Mac OS X 10.5.8 or later version with Intel chip.
- Linux including GNU C Library 2.7 or later.
- Java JDK5 or later version
- Android SDK
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 6
- Android Studio
- Eclipse IDE for Java Developers (optional)
- Android Development Tools (ADT) Eclipse Plug-in (optional)
Set-up Java Development Kit (JDK)
You can download the latest version of Java JDK from Oracle's Java site: Java SE Downloads. You will find instructions for installing JDK in downloaded files, follow the given instructions to install and configure the setup. Finally set PATH and JAVA_HOME environment variables to refer to the directory that contains java and javac, typically java_install_dir/bin and java_install_dir respectively.If you are running Windows and installed the JDK in C:\jdk1.6.0_15, you would have to put the following line in your C:\autoexec.bat file.
set PATH=C:\jdk1.7.0_75\bin;%PATH% set JAVA_HOME=C:\jdk1.7.0_75Alternatively, you could also right-click on My Computer, select Properties, then Advanced, then Environment Variables. Then, you would update the PATH value and press the OK button.
On Linux, if the SDK is installed in /usr/local/jdk1.6.0_15 and you use the C shell, you would put the following code into your .cshrc file.
setenv PATH /usr/local/jdk1.7.0_75/bin:$PATH setenv JAVA_HOME /usr/local/jdk1.7.0_75Alternatively, if you use an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) Eclipse, then it will know automatically where you have installed your Java.
Android IDEs
There are so many sophisticated Technologies are available to develop android applications, the familiar technologies, which are predominantly using tools as follows- Android Studio
- Eclipse IDE
Android - Architecture
Android operating system is a stack of software components which is roughly divided into five sections and four main layers as shown below in the architecture diagram.

Linux kernel
At the bottom of the layers is Linux - Linux 3.6 with approximately 115 patches. This provides a level of abstraction between the device hardware and it contains all the essential hardware drivers like camera, keypad, display etc. Also, the kernel handles all the things that Linux is really good at such as networking and a vast array of device drivers, which take the pain out of interfacing to peripheral hardware.
Libraries
On top of Linux kernel there is a set of libraries including open-source Web browser engine WebKit, well known library libc, SQLite database which is a useful repository for storage and sharing of application data, libraries to play and record audio and video, SSL libraries responsible for Internet security etc.
Android Libraries
This category encompasses those Java-based libraries that are specific to Android development. Examples of libraries in this category include the application framework libraries in addition to those that facilitate user interface building, graphics drawing and database access. A summary of some key core Android libraries available to the Android developer is as follows −
- android.app − Provides access to the application model and is the cornerstone of all Android applications.
- android.content − Facilitates content access, publishing and messaging between applications and application components.
- android.database − Used to access data published by content providers and includes SQLite database management classes.
- android.opengl − A Java interface to the OpenGL ES 3D graphics rendering API.
- android.os − Provides applications with access to standard operating system services including messages, system services and inter-process communication.
- android.text − Used to render and manipulate text on a device display.
- android.view − The fundamental building blocks of application user interfaces.
- android.widget − A rich collection of pre-built user interface components such as buttons, labels, list views, layout managers, radio buttons etc.
- android.webkit − A set of classes intended to allow web-browsing capabilities to be built into applications.
Android Runtime
This is the third section of the architecture and available on the second layer from the bottom. This section provides a key component called Dalvik Virtual Machine which is a kind of Java Virtual Machine specially designed and optimized for Android.The Dalvik VM makes use of Linux core features like memory management and multi-threading, which is intrinsic in the Java language. The Dalvik VM enables every Android application to run in its own process, with its own instance of the Dalvik virtual machine.
The Android runtime also provides a set of core libraries which enable Android application developers to write Android applications using standard Java programming language.
Application Framework
The Application Framework layer provides many higher-level services to applications in the form of Java classes. Application developers are allowed to make use of these services in their applications.The Android framework includes the following key services −
- Activity Manager − Controls all aspects of the application lifecycle and activity stack.
- Content Providers − Allows applications to publish and share data with other applications.
- Resource Manager − Provides access to non-code embedded resources such as strings, color settings and user interface layouts.
- Notifications Manager − Allows applications to display alerts and notifications to the user.
- View System − An extensible set of views used to create application user interfaces.
Applications
You will find all the Android application at the top layer. You will write your application to be installed on this layer only. Examples of such applications are Contacts Books, Browser, Games etc.Android - Application Components
Application components are the essential building blocks of an Android application. These components are loosely coupled by the application manifest file AndroidManifest.xml that describes each component of the application and how they interact.There are following four main components that can be used within an Android application:
| Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Activities | They dictate the UI and handle the user interaction to the smart phone screen |
| Services | They handle background processing associated with an application. |
| Broadcast Receivers | They handle communication between Android OS and applications. |
| Content Providers | They handle data and database management issues. |
Activities
An activity represents a single screen with a user interface,in-short Activity performs actions on the screen. For example, an email application might have one activity that shows a list of new emails, another activity to compose an email, and another activity for reading emails. If an application has more than one activity, then one of them should be marked as the activity that is presented when the application is launched.An activity is implemented as a subclass of Activity class as follows −
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
}
Services
A service is a component that runs in the background to perform long-running operations. For example, a service might play music in the background while the user is in a different application, or it might fetch data over the network without blocking user interaction with an activity.A service is implemented as a subclass of Service class as follows −
public class MyService extends Service {
}
Broadcast Receivers
Broadcast Receivers simply respond to broadcast messages from other applications or from the system. For example, applications can also initiate broadcasts to let other applications know that some data has been downloaded to the device and is available for them to use, so this is broadcast receiver who will intercept this communication and will initiate appropriate action.A broadcast receiver is implemented as a subclass of BroadcastReceiver class and each message is broadcaster as an Intent object.
public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
public void onReceive(context,intent){}
}
Content Providers
A content provider component supplies data from one application to others on request. Such requests are handled by the methods of the ContentResolver class. The data may be stored in the file system, the database or somewhere else entirely.A content provider is implemented as a subclass of ContentProvider class and must implement a standard set of APIs that enable other applications to perform transactions.
public class MyContentProvider extends ContentProvider {
public void onCreate(){}
}
We will go through these tags in detail while covering application components in individual chapters.Additional Components
There are additional components which will be used in the construction of above mentioned entities, their logic, and wiring between them. These components are −| Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Fragments | Represents a portion of user interface in an Activity. |
| Views | UI elements that are drawn on-screen including buttons, lists forms etc. |
| Layouts | View hierarchies that control screen format and appearance of the views. |
| Intents | Messages wiring components together. |
| Resources | External elements, such as strings, constants and drawable pictures. |
| Manifest | Configuration file for the application. |
Let us start actual programming with Android Framework. Before you start writing your first example using Android SDK, you have to make sure that you have set-up your Android development environment properly as explained in Android - Environment Set-up tutorial. I also assume that you have a little bit working knowledge with Eclipse IDE.
So let us proceed to write a simple Android Application which will print "Hello World!".
Create Android Application
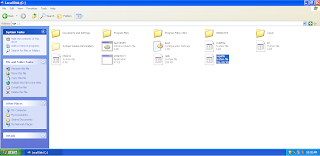
The first step is to create a simple Android Application using Eclipse IDE. Follow the option File -> New -> Project and finally select Android New Application wizard from the wizard list. Now name your application as HelloWorld using the wizard window as follows: Next, follow the instructions provided and keep all other entries as
default till the final step. Once your project is created successfully,
you will have following project screen −
Next, follow the instructions provided and keep all other entries as
default till the final step. Once your project is created successfully,
you will have following project screen −
Anatomy of Android Application
Before you run your app, you should be aware of a few directories and files in the Android project −
| S.N. | Folder, File & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | src This contains the .java source files for your project. By default, it includes an MainActivity.java source file having an activity class that runs when your app is launched using the app icon. |
| 2 | gen This contains the .R file, a compiler-generated file that references all the resources found in your project. You should not modify this file. |
| 3 | bin This folder contains the Android package files .apk built by the ADT during the build process and everything else needed to run an Android application. |
| 4 | res/drawable-hdpi This is a directory for drawable objects that are designed for high-density screens. |
| 5 | res/layout This is a directory for files that define your app's user interface. |
| 6 | res/values This is a directory for other various XML files that contain a collection of resources, such as strings and colours definitions. |
| 7 | AndroidManifest.xml This is the manifest file which describes the fundamental characteristics of the app and defines each of its components. |
The Main Activity File
The main activity code is a Java file MainActivity.java. This is the actual application file which ultimately gets converted to a Dalvik executable and runs your application. Following is the default code generated by the application wizard for Hello World! application −package com.example.helloworld; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuItem; import android.support.v4.app.NavUtils; public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu); return true; } }Here, R.layout.activity_main refers to the activity_main.xml file located in the res/layout folder. The onCreate() method is one of many methods that are figured when an activity is loaded.
The Manifest File
Whatever component you develop as a part of your application, you must declare all its components in a manifest.xml which resides at the root of the application project directory. This file works as an interface between Android OS and your application, so if you do not declare your component in this file, then it will not be considered by the OS. For example, a default manifest file will look like as following file −<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.helloworld" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="22" /> <application android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/title_activity_main" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>Here <application>...</application> tags enclosed the components related to the application. Attribute android:icon will point to the application icon available under res/drawable-hdpi. The application uses the image named ic_launcher.png located in the drawable folders
The <activity> tag is used to specify an activity and android:name attribute specifies the fully qualified class name of the Activity subclass and the android:label attributes specifies a string to use as the label for the activity. You can specify multiple activities using <activity> tags.
The action for the intent filter is named android.intent.action.MAIN to indicate that this activity serves as the entry point for the application. The category for the intent-filter is named android.intent.category.LAUNCHER to indicate that the application can be launched from the device's launcher icon.
The @string refers to the strings.xml file explained below. Hence, @string/app_name refers to the app_name string defined in the strings.xml file, which is "HelloWorld". Similar way, other strings get populated in the application.
Following is the list of tags which you will use in your manifest file to specify different Android application components:
- <activity>elements for activities
- <service> elements for services
- <receiver> elements for broadcast receivers
- <provider> elements for content providers
The Strings File
The strings.xml file is located in the res/values folder and it contains all the text that your application uses. For example, the names of buttons, labels, default text, and similar types of strings go into this file. This file is responsible for their textual content. For example, a default strings file will look like as following file −<resources> <string name="app_name">HelloWorld</string> <string name="hello_world">Hello world!</string> <string name="menu_settings">Settings</string> <string name="title_activity_main">MainActivity</string> </resources>
The R File
The gen/com.example.helloworld/R.java file is the glue between the activity Java files like MainActivity.java and the resources like strings.xml. It is an automatically generated file and you should not modify the content of the R.java file. Following is a sample of R.java file −/* AUTO-GENERATED FILE. DO NOT MODIFY. * * This class was automatically generated by the * aapt tool from the resource data it found. It * should not be modified by hand. */ package com.example.helloworld; public final class R { public static final class attr { } public static final class dimen { public static final int padding_large=0x7f040002; public static final int padding_medium=0x7f040001; public static final int padding_small=0x7f040000; } public static final class drawable { public static final int ic_action_search=0x7f020000; public static final int ic_launcher=0x7f020001; } public static final class id { public static final int menu_settings=0x7f080000; } public static final class layout { public static final int activity_main=0x7f030000; } public static final class menu { public static final int activity_main=0x7f070000; } public static final class string { public static final int app_name=0x7f050000; public static final int hello_world=0x7f050001; public static final int menu_settings=0x7f050002; public static final int title_activity_main=0x7f050003; } public static final class style { public static final int AppTheme=0x7f060000; } }
The Layout File
The activity_main.xml is a layout file available in res/layout directory, that is referenced by your application when building its interface. You will modify this file very frequently to change the layout of your application. For your "Hello World!" application, this file will have following content related to default layout −<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:padding="@dimen/padding_medium" android:text="@string/hello_world" tools:context=".MainActivity" /> </RelativeLayout>This is an example of simple RelativeLayout which we will study in a separate chapter. The TextView is an Android control used to build the GUI and it have various attributes like android:layout_width, android:layout_height etc which are being used to set its width and height etc.. The @string refers to the strings.xml file located in the res/values folder. Hence, @string/hello_world refers to the hello string defined in the strings.xml file, which is "Hello World!".
Running the Application
Let's try to run our Hello World! application we just created. I assume you had created your AVD while doing environment set-up. To run the app from Eclipse, open one of your project's activity files and click Run icon from the tool bar. Eclipse installs the app on your AVD and starts
it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application, it will
display following Emulator window −
icon from the tool bar. Eclipse installs the app on your AVD and starts
it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application, it will
display following Emulator window − Congratulations!!! you have developed your first Android Application
and now just keep following rest of the tutorial step by step to become a
great Android Developer. All the very best.
Congratulations!!! you have developed your first Android Application
and now just keep following rest of the tutorial step by step to become a
great Android Developer. All the very best.Create Android Application on Android studio
There are so many tools are available to develop android applications. as per Google official android development, they have launched android studio as official Android IDE- Hello World
Android Resources Organizing & Accessing
There are many more items which you use to build a good Android application. Apart from coding for the application, you take care of various other resources like static content that your code uses, such as bitmaps, colors, layout definitions, user interface strings, animation instructions, and more. These resources are always maintained separately in various sub-directories under res/ directory of the project.
This tutorial will explain you how you can organize your application resources, specify alternative resources and access them in your applications.
Organize Resources in eclipse
You should place each type of resource in a specific sub directory of your project's res/ directory. For example, here's the file hierarchy for a simple project:
MyProject/ src/ MyActivity.java res/ drawable/ icon.png layout/ activity_main.xml info.xml values/ strings.xmlThe res/ directory contains all the resources in various sub directories. Here we have an image resource, two layout resources, and a string resource file. Following table gives a detail about the resource directories supported inside project res/ directory.
Organize resource in Android Studio
MyProject/ src/ main/ java/ MyActivity.java res/ drawable/ icon.png layout/ activity_main.xml info.xml values/ strings.xmlDirectory Resource Type anim/ XML files that define property animations. They are saved in res/anim/ folder and accessed from the R.anim class. color/ XML files that define a state list of colors. They are saved in res/color/ and accessed from the R.color class. drawable/ Image files like .png, .jpg, .gif or XML files that are compiled into bitmaps, state lists, shapes, animation drawable. They are saved in res/drawable/ and accessed from the R.drawable class. layout/ XML files that define a user interface layout. They are saved in res/layout/ and accessed from the R.layout class. menu/ XML files that define application menus, such as an Options Menu, Context Menu, or Sub Menu. They are saved in res/menu/ and accessed from the R.menu class. raw/ Arbitrary files to save in their raw form. You need to call Resources.openRawResource() with the resource ID, which is R.raw.filename to open such raw files. values/ XML files that contain simple values, such as strings, integers, and colors. For example, here are some filename conventions for resources you can create in this directory −
- arrays.xml for resource arrays, and accessed from the R.array class.
- integers.xml for resource integers, and accessed from the R.integer class.
- bools.xml for resource boolean, and accessed from the R.bool class.
- colors.xml for color values, and accessed from the R.color class.
- dimens.xml for dimension values, and accessed from the R.dimen class.
- strings.xml for string values, and accessed from the R.string class.
- styles.xml for styles, and accessed from the R.style class.
xml/ Arbitrary XML files that can be read at runtime by calling Resources.getXML(). You can save various configuration files here which will be used at run time. Alternative Resources
Your application should provide alternative resources to support specific device configurations. For example, you should include alternative drawable resources ( i.e.images ) for different screen resolution and alternative string resources for different languages. At runtime, Android detects the current device configuration and loads the appropriate resources for your application.
To specify configuration-specific alternatives for a set of resources, follow the following steps −
- Create a new directory in res/ named in the form <resources_name>-<config_qualifier>. Here resources_name will be any of the resources mentioned in the above table, like layout, drawable etc. The qualifier will specify an individual configuration for which these resources are to be used. You can check official documentation for a complete list of qualifiers for different type of resources.
- Save the respective alternative resources in this new directory. The resource files must be named exactly the same as the default resource files as shown in the below example, but these files will have content specific to the alternative. For example though image file name will be same but for high resolution screen, its resolution will be high.
MyProject/
src/
main/
java/
MyActivity.java
res/
drawable/
icon.png
background.png
drawable-hdpi/
icon.png
background.png
layout/
activity_main.xml
info.xml
values/
strings.xml
Below is another example which specifies layout for a default language and alternative layout for Arabic language.MyProject/
src/
main/
java/
MyActivity.java
res/
drawable/
icon.png
background.png
drawable-hdpi/
icon.png
background.png
layout/
activity_main.xml
info.xml
layout-ar/
main.xml
values/
strings.xml
Accessing Resources
During your application development you will need to access defined resources either in your code, or in your layout XML files. Following section explains how to access your resources in both the scenarios −Accessing Resources in Code
When your Android application is compiled, a R class gets generated, which contains resource IDs for all the resources available in your res/ directory. You can use R class to access that resource using sub-directory and resource name or directly resource ID.Example
To access res/drawable/myimage.png and set an ImageView you will use following code:ImageView imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.myimageview); imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.myimage);Here first line of the code make use of R.id.myimageview to get ImageView defined with id myimageview in a Layout file. Second line of code makes use of R.drawable.myimage to get an image with name myimage available in drawable sub-directory under /res.
Example
Consider next example where res/values/strings.xml has following definition:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="hello">Hello, World!</string>
</resources>
Now you can set the text on a TextView object with ID msg using a resource ID as follows:TextView msgTextView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.msg); msgTextView.setText(R.string.hello);
Example
Consider a layout res/layout/activity_main.xml with the following definition:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello, I am a TextView" />
<Button android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello, I am a Button" />
</LinearLayout>
This application code will load this layout for an Activity, in the onCreate() method as follows −public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main_activity);
}
Accessing Resources in XML
Consider the following resource XML res/values/strings.xml file that includes a color resource and a string resource −<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <color name="opaque_red">#f00</color> <string name="hello">Hello!</string> </resources>Now you can use these resources in the following layout file to set the text color and text string as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<EditText xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:textColor="@color/opaque_red"
android:text="@string/hello" />
Now if you will go through previous chapter once again where I have explained Hello World!
example, and I'm sure you will have better understanding on all the
concepts explained in this chapter. So I highly recommend to check
previous chapter for working example and check how I have used various
resources at very basic level.Android - Activities
An activity represents a single screen with a user interface just like window or frame of Java.Android activity is the subclass of ContextThemeWrapper class.If you have worked with C, C++ or Java programming language then you must have seen that your program starts from main() function. Very similar way, Android system initiates its program with in an Activity starting with a call on onCreate() callback method. There is a sequence of callback methods that start up an activity and a sequence of callback methods that tear down an activity as shown in the below Activity life cycle diagram: (image courtesy : android.com )
 The Activity class defines the following call backs i.e. events. You
don't need to implement all the callbacks methods. However, it's
important that you understand each one and implement those that ensure
your app behaves the way users expect.
The Activity class defines the following call backs i.e. events. You
don't need to implement all the callbacks methods. However, it's
important that you understand each one and implement those that ensure
your app behaves the way users expect.| Callback | Description |
|---|---|
| onCreate() | This is the first callback and called when the activity is first created. |
| onStart() | This callback is called when the activity becomes visible to the user. |
| onResume() | This is called when the user starts interacting with the application. |
| onPause() | The paused activity does not receive user input and cannot execute any code and called when the current activity is being paused and the previous activity is being resumed. |
| onStop() | This callback is called when the activity is no longer visible. |
| onDestroy() | This callback is called before the activity is destroyed by the system. |
| onRestart() | This callback is called when the activity restarts after stopping it. |
Example
This example will take you through simple steps to show Android application activity life cycle. Follow the following steps to modify the Android application we created in Hello World Example chapter:| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | You will use eclipse IDE to create an Android application and name it as HelloWorld under a package com.example.helloworld as explained in the Hello World Example chapter. |
| 2 | Modify main activity file MainActivity.java as explained below. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
| 3 | Run the application to launch Android emulator and verify the result of the changes done in the application. |
package com.example.helloworld;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.util.Log;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
String msg = "Android : ";
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.d(msg, "The onCreate() event");
}
/** Called when the activity is about to become visible. */
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
Log.d(msg, "The onStart() event");
}
/** Called when the activity has become visible. */
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
Log.d(msg, "The onResume() event");
}
/** Called when another activity is taking focus. */
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
Log.d(msg, "The onPause() event");
}
/** Called when the activity is no longer visible. */
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
Log.d(msg, "The onStop() event");
}
/** Called just before the activity is destroyed. */
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d(msg, "The onDestroy() event");
}
}
An activity class loads all the UI component using the XML file available in res/layout folder of the project. Following statement loads UI components from res/layout/activity_main.xml file:setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);An application can have one or more activities without any restrictions. Every activity you define for your application must be declared in your AndroidManifest.xml file and the main activity for your app must be declared in the manifest with an <intent-filter> that includes the MAIN action and LAUNCHER category as follows:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.helloworld"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="22" />
<application
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/title_activity_main" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
If either the MAIN action or LAUNCHER category are not declared for
one of your activities, then your app icon will not appear in the Home
screen's list of apps.Let's try to run our modified Hello World! application we just modified. I assume you had created your AVD while doing environment setup. To run the app from Eclipse, open one of your project's activity files and click Run
 icon from the toolbar. Eclipse installs the app on your AVD and starts
it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it will
display Emulator window and you should see following log messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:
icon from the toolbar. Eclipse installs the app on your AVD and starts
it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it will
display Emulator window and you should see following log messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:07-19 15:00:43.405: D/Android :(866): The onCreate() event 07-19 15:00:43.405: D/Android :(866): The onStart() event 07-19 15:00:43.415: D/Android :(866): The onResume() event
 Let us try to click Red button
Let us try to click Red button  on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:
on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:07-19 15:01:10.995: D/Android :(866): The onPause() event 07-19 15:01:12.705: D/Android :(866): The onStop() eventLet us again try to click Menu button
 on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:
on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE:07-19 15:01:13.995: D/Android :(866): The onStart() event 07-19 15:01:14.705: D/Android :(866): The onResume() eventNext, let us again try to click Back button
 on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE and this completes the Activity Life Cycle for an Android Application.
on the Android emulator and it will generate following events messages in LogCat window in Eclipse IDE and this completes the Activity Life Cycle for an Android Application.07-19 15:33:15.687: D/Android :(992): The onPause() event 07-19 15:33:15.525: D/Android :(992): The onStop() event 07-19 15:33:15.525: D/Android :(992): The onDestroy() event
Android - Services
A service is a component that runs in the background to perform long-running operations without needing to interact with the user and it works even if application is destroyed. A service can essentially take two states −
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| Started | A service is started when an application component, such as an activity, starts it by calling startService(). Once started, a service can run in the background indefinitely, even if the component that started it is destroyed. |
| Bound | A service is bound when an application component binds to it by calling bindService(). A bound service offers a client-server interface that allows components to interact with the service, send requests, get results, and even do so across processes with interprocess communication (IPC). |
 To create an service, you create a Java class that extends the Service base class or one of its existing subclasses. The Service
base class defines various callback methods and the most important are
given below. You don't need to implement all the callbacks methods.
However, it's important that you understand each one and implement those
that ensure your app behaves the way users expect.
To create an service, you create a Java class that extends the Service base class or one of its existing subclasses. The Service
base class defines various callback methods and the most important are
given below. You don't need to implement all the callbacks methods.
However, it's important that you understand each one and implement those
that ensure your app behaves the way users expect.| Callback | Description |
|---|---|
| onStartCommand() | The system calls this method when another component, such as an activity, requests that the service be started, by calling startService(). If you implement this method, it is your responsibility to stop the service when its work is done, by calling stopSelf() or stopService() methods. |
| onBind() | The system calls this method when another component wants to bind with the service by calling bindService(). If you implement this method, you must provide an interface that clients use to communicate with the service, by returning an IBinder object. You must always implement this method, but if you don't want to allow binding, then you should return null. |
| onUnbind() | The system calls this method when all clients have disconnected from a particular interface published by the service. |
| onRebind() | The system calls this method when new clients have connected to the service, after it had previously been notified that all had disconnected in its onUnbind(Intent). |
| onCreate() | The system calls this method when the service is first created using onStartCommand() or onBind(). This call is required to perform one-time set-up. |
| onDestroy() | The system calls this method when the service is no longer used and is being destroyed. Your service should implement this to clean up any resources such as threads, registered listeners, receivers, etc. |
package com.tutorialspoint;
import android.app.Service;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class HelloService extends Service {
/** indicates how to behave if the service is killed */
int mStartMode;
/** interface for clients that bind */
IBinder mBinder;
/** indicates whether onRebind should be used */
boolean mAllowRebind;
/** Called when the service is being created. */
@Override
public void onCreate() {
}
/** The service is starting, due to a call to startService() */
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
return mStartMode;
}
/** A client is binding to the service with bindService() */
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
/** Called when all clients have unbound with unbindService() */
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
return mAllowRebind;
}
/** Called when a client is binding to the service with bindService()*/
@Override
public void onRebind(Intent intent) {
}
/** Called when The service is no longer used and is being destroyed */
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
}
}
Example
This example will take you through simple steps to show how to create your own Android Service. Follow the following steps to modify the Android application we created in Hello World Example chapter:| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | You will use Android StudioIDE to create an Android application and name it as My Application under a package com.example.My Application as explained in the Hello World Example chapter. |
| 2 | Modify main activity file MainActivity.java to add startService() and stopService() methods. |
| 3 | Create a new java file MyService.java under the package com.example.My Application. This file will have implementation of Android service related methods. |
| 4 | Define your service in AndroidManifest.xml file using <service.../> tag. An application can have one or more services without any restrictions. |
| 5 | Modify the default content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file to include two buttons in linear layout. |
| 6 | No need to change any constants in res/values/strings.xml file. Android studio take care of string values |
| 7 | Run the application to launch Android emulator and verify the result of the changes done in the application. |
package com.example.My Application;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu);
return true;
}
// Method to start the service
public void startService(View view) {
startService(new Intent(getBaseContext(), MyService.class));
}
// Method to stop the service
public void stopService(View view) {
stopService(new Intent(getBaseContext(), MyService.class));
}
}
Following is the content of src/com.example.My Application/MyService.java.
This file can have implementation of one or more methods associated
with Service based on requirements. For now we are going to implement
only two methods onStartCommand() and onDestroy() −package com.example.My Application;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MyService extends Service {
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
return null;
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// Let it continue running until it is stopped.
Toast.makeText(this, "Service Started", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Toast.makeText(this, "Service Destroyed", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
Following will the modified content of AndroidManifest.xml file. Here we have added <service.../> tag to include our service:<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.MyApplication"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="13"
android:targetSdkVersion="22" />
<application
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/title_activity_main" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".MyService" />
</application>
</manifest>
Following will be the content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file to include two buttons:<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Example of services"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:textSize="30dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tutorials point "
android:textColor="#ff87ff09"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:layout_above="@+id/imageButton"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="40dp" />
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/imageButton"
android:src="@drawable/abc"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:text="Start Services"
android:onClick="startService"
android:layout_below="@+id/imageButton"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Stop Services"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:onClick="stopService"
android:layout_below="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/button2" />
</RelativeLayout>
Following will be the content of res/values/strings.xml to define two new constants:<resources>
<string name="app_name">My Application</string>
<string name="menu_settings">Settings</string>
<string name="title_activity_main">MainActivity</string>
</resources>
Let's try to run our modified Hello World! application we just modified. I assume you had created your AVD while doing environment setup. To run the app from Android studio, open one of your project's activity files and click Run  icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window −
icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window − Now to start your service, let's click on Start Service button, this will start the service and as per our programming in onStartCommand() method, a message Service Started will appear on the bottom of the the simulator as follows −
Now to start your service, let's click on Start Service button, this will start the service and as per our programming in onStartCommand() method, a message Service Started will appear on the bottom of the the simulator as follows − To stop the service, you can click the Stop Service button.
To stop the service, you can click the Stop Service button.Android - Broadcast Receivers
Broadcast Receivers simply respond to broadcast messages from other applications or from the system itself. These messages are sometime called events or intents. For example, applications can also initiate broadcasts to let other applications know that some data has been downloaded to the device and is available for them to use, so this is broadcast receiver who will intercept this communication and will initiate appropriate action.There are following two important steps to make BroadcastReceiver works for the system broadcasted intents −
- Creating the Broadcast Receiver.
- Registering Broadcast Receiver
Creating the Broadcast Receiver
A broadcast receiver is implemented as a subclass of BroadcastReceiver class and overriding the onReceive() method where each message is received as a Intent object parameter.public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver { @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { Toast.makeText(context, "Intent Detected.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } }
Registering Broadcast Receiver
An application listens for specific broadcast intents by registering a broadcast receiver in AndroidManifest.xml file. Consider we are going to register MyReceiver for system generated event ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED which is fired by the system once the Android system has completed the boot process.
Broadcast-Receiver
<application android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <receiver android:name="MyReceiver"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED"> </action> </intent-filter> </receiver> </application>Now whenever your Android device gets booted, it will be intercepted by BroadcastReceiver MyReceiver and implemented logic inside onReceive() will be executed.
There are several system generated events defined as final static fields in the Intent class. The following table lists a few important system events.
| Event Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| android.intent.action.BATTERY_CHANGED | Sticky broadcast containing the charging state, level, and other information about the battery. |
| android.intent.action.BATTERY_LOW | Indicates low battery condition on the device. |
| android.intent.action.BATTERY_OKAY | Indicates the battery is now okay after being low. |
| android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED | This is broadcast once, after the system has finished booting. |
| android.intent.action.BUG_REPORT | Show activity for reporting a bug. |
| android.intent.action.CALL | Perform a call to someone specified by the data. |
| android.intent.action.CALL_BUTTON | The user pressed the "call" button to go to the dialer or other appropriate UI for placing a call. |
| android.intent.action.DATE_CHANGED | The date has changed. |
| android.intent.action.REBOOT | Have the device reboot. |
Broadcasting Custom Intents
If you want your application itself should generate and send custom intents then you will have to create and send those intents by using the sendBroadcast() method inside your activity class. If you use the sendStickyBroadcast(Intent) method, the Intent is sticky, meaning the Intent you are sending stays around after the broadcast is complete.public void broadcastIntent(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"); sendBroadcast(intent); }This intent com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT can also be registered in similar way as we have regsitered system generated intent.
<application android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <receiver android:name="MyReceiver"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"> </action> </intent-filter> </receiver> </application>
Example
This example will explain you how to create BroadcastReceiver to intercept custom intent. Once you are familiar with custom intent, then you can program your application to intercept system generated intents. So let's follow the following steps to modify the Android application we created in Hello World Example chapter −| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | You will use Android studio to create an Android application and name it as My Application under a package com.example.My Application as explained in the Hello World Example chapter. |
| 2 | Modify main activity file MainActivity.java to add broadcastIntent() method. |
| 3 | Create a new java file called MyReceiver.java under the package com.example.My Application to define a BroadcastReceiver. |
| 4 | An application can handle one or more custom and system intents without any restrictions. Every indent you want to intercept must be registered in your AndroidManifest.xml file using <receiver.../> tag |
| 5 | Modify the default content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file to include a button to broadcast intent. |
| 6 | No need to modify the string file, Android studio take care of string.xml file. |
| 7 | Run the application to launch Android emulator and verify the result of the changes done in the application. |
package com.example.My Application; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.view.Menu; import android.content.Intent; import android.view.View; public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu); return true; } // broadcast a custom intent. public void broadcastIntent(View view){ Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"); sendBroadcast(intent); } }Following is the content of src/com.example.My Application/MyReceiver.java:
package com.example.My Application; import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.widget.Toast; public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver { @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { Toast.makeText(context, "Intent Detected.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } }Following will the modified content of AndroidManifest.xml file. Here we have added <service.../> tag to include our service:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.My Application" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="22" /> <application android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/title_activity_main" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/> </intent-filter> </activity> <receiver android:name="MyReceiver"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"> </action> </intent-filter> </receiver> </application> </manifest>Following will be the content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file to include a button to broadcast our custom intent −
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Example of Broadcast" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:textSize="30dp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Tutorials point " android:textColor="#ff87ff09" android:textSize="30dp" android:layout_above="@+id/imageButton" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginBottom="40dp" /> <ImageButton android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/imageButton" android:src="@drawable/abc" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/button2" android:text="Broadcast Intent" android:onClick="broadcastIntent" android:layout_below="@+id/imageButton" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> </RelativeLayout>Following will be the content of res/values/strings.xml to define two new constants −
<resources> <string name="menu_settings">Settings</string> <string name="title_activity_main">My Application</string> </resources>Let's try to run our modified Hello World! application we just modified. I assume you had created your AVD while doing environment set-up. To run the app from Android studio, open one of your project's activity files and click Run
 icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window −
icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window − Now to broadcast our custom intent, let's click on Broadcast Intent button, this will broadcast our custom intent "com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"
which will be intercepted by our registered BroadcastReceiver i.e.
MyReceiver and as per our implemented logic a toast will appear on the
bottom of the the simulator as follows −
Now to broadcast our custom intent, let's click on Broadcast Intent button, this will broadcast our custom intent "com.tutorialspoint.CUSTOM_INTENT"
which will be intercepted by our registered BroadcastReceiver i.e.
MyReceiver and as per our implemented logic a toast will appear on the
bottom of the the simulator as follows − You can try implementing other BroadcastReceiver to intercept system
generated intents like system boot up, date changed, low battery etc.
You can try implementing other BroadcastReceiver to intercept system
generated intents like system boot up, date changed, low battery etc.Android - Content Providers
A content provider component supplies data from one application to others on request. Such requests are handled by the methods of the ContentResolver class. A content provider can use different ways to store its data and the data can be stored in a database, in files, or even over a network.

ContentProvider
sometimes it is required to share data across applications. This is where content providers become very useful.Content providers let you centralize content in one place and have many different applications access it as needed. A content provider behaves very much like a database where you can query it, edit its content, as well as add or delete content using insert(), update(), delete(), and query() methods. In most cases this data is stored in an SQlite database.
A content provider is implemented as a subclass of ContentProvider class and must implement a standard set of APIs that enable other applications to perform transactions.
public class My Application extends ContentProvider {
}
Content URIs
To query a content provider, you specify the query string in the form of a URI which has following format:<prefix>://<authority>/<data_type>/<id>Here is the detail of various parts of the URI −
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| prefix | This is always set to content:// |
| authority | This specifies the name of the content provider, for example contacts, browser etc. For third-party content providers, this could be the fully qualified name, such as com.tutorialspoint.statusprovider |
| data_type | This indicates the type of data that this particular provider provides. For example, if you are getting all the contacts from the Contacts content provider, then the data path would be people and URI would look like this content://contacts/people |
| id | This specifies the specific record requested. For example, if you are looking for contact number 5 in the Contacts content provider then URI would look like this content://contacts/people/5. |
Create Content Provider
This involves number of simple steps to create your own content provider.- First of all you need to create a Content Provider class that extends the ContentProviderbaseclass.
- Second, you need to define your content provider URI address which will be used to access the content.
- Next you will need to create your own database to keep the content. Usually, Android uses SQLite database and framework needs to override onCreate() method which will use SQLite Open Helper method to create or open the provider's database. When your application is launched, the onCreate() handler of each of its Content Providers is called on the main application thread.
- Next you will have to implement Content Provider queries to perform different database specific operations.
- Finally register your Content Provider in your activity file using <provider> tag.

ContentProvider
- onCreate() This method is called when the provider is started.
- query() This method receives a request from a client. The result is returned as a Cursor object.
- insert()This method inserts a new record into the content provider.
- delete() This method deletes an existing record from the content provider.
- update() This method updates an existing record from the content provider.
- getType() This method returns the MIME type of the data at the given URI.
Example
This example will explain you how to create your own ContentProvider. So let's follow the following steps to similar to what we followed while creating Hello World Example−| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | You will use Android StudioIDE to create an Android application and name it as My Application under a package com.example.My Application, with blank Activity. |
| 2 | Modify main activity file MainActivity.java to add two new methods onClickAddName() and onClickRetrieveStudents(). |
| 3 | Create a new java file called StudentsProvider.java under the package com.example.My Application to define your actual provider and associated methods. |
| 4 | Register your content provider in your AndroidManifest.xml file using <provider.../> tag |
| 5 | Modify the default content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file to include a small GUI to add students records. |
| 6 | No need to change string.xml.Android studio take care of string.xml file. |
| 7 | Run the application to launch Android emulator and verify the result of the changes done in the application. |
package com.example.My Application;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.CursorLoader;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
public void onClickAddName(View view) {
// Add a new student record
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(StudentsProvider.NAME,
((EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText2)).getText().toString());
values.put(StudentsProvider.GRADE,
((EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText3)).getText().toString());
Uri uri = getContentResolver().insert(
StudentsProvider.CONTENT_URI, values);
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(),
uri.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
public void onClickRetrieveStudents(View view) {
// Retrieve student records
String URL = "content://com.example.provider.College/students";
Uri students = Uri.parse(URL);
Cursor c = managedQuery(students, null, null, null, "name");
if (c.moveToFirst()) {
do{
Toast.makeText(this,
c.getString(c.getColumnIndex(StudentsProvider._ID)) +
", " + c.getString(c.getColumnIndex( StudentsProvider.NAME)) +
", " + c.getString(c.getColumnIndex( StudentsProvider.GRADE)),
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} while (c.moveToNext());
}
}
}
Create new file StudentsProvider.java under com.example.My Application package and following is the content of src/com.example.My Application/StudentsProvider.java −package com.example.My Application;
import java.util.HashMap;
import android.content.ContentProvider;
import android.content.ContentUris;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.UriMatcher;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.SQLException;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteQueryBuilder;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.text.TextUtils;
public class StudentsProvider extends ContentProvider {
static final String PROVIDER_NAME = "com.example.provider.College";
static final String URL = "content://" + PROVIDER_NAME + "/students";
static final Uri CONTENT_URI = Uri.parse(URL);
static final String _ID = "_id";
static final String NAME = "name";
static final String GRADE = "grade";
private static HashMap<String, String> STUDENTS_PROJECTION_MAP;
static final int STUDENTS = 1;
static final int STUDENT_ID = 2;
static final UriMatcher uriMatcher;
static{
uriMatcher = new UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH);
uriMatcher.addURI(PROVIDER_NAME, "students", STUDENTS);
uriMatcher.addURI(PROVIDER_NAME, "students/#", STUDENT_ID);
}
/**
* Database specific constant declarations
*/
private SQLiteDatabase db;
static final String DATABASE_NAME = "College";
static final String STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME = "students";
static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 1;
static final String CREATE_DB_TABLE =
" CREATE TABLE " + STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME +
" (_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, " +
" name TEXT NOT NULL, " +
" grade TEXT NOT NULL);";
/**
* Helper class that actually creates and manages
* the provider's underlying data repository.
*/
private static class DatabaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
DatabaseHelper(Context context){
super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db)
{
db.execSQL(CREATE_DB_TABLE);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
db.execSQL("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS " + STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME);
onCreate(db);
}
}
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
Context context = getContext();
DatabaseHelper dbHelper = new DatabaseHelper(context);
/**
* Create a write able database which will trigger its
* creation if it doesn't already exist.
*/
db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
return (db == null)? false:true;
}
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
/**
* Add a new student record
*/
long rowID = db.insert( STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME, "", values);
/**
* If record is added successfully
*/
if (rowID > 0)
{
Uri _uri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(CONTENT_URI, rowID);
getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(_uri, null);
return _uri;
}
throw new SQLException("Failed to add a record into " + uri);
}
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection,String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
SQLiteQueryBuilder qb = new SQLiteQueryBuilder();
qb.setTables(STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME);
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)) {
case STUDENTS:
qb.setProjectionMap(STUDENTS_PROJECTION_MAP);
break;
case STUDENT_ID:
qb.appendWhere( _ID + "=" + uri.getPathSegments().get(1));
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI " + uri);
}
if (sortOrder == null || sortOrder == ""){
/**
* By default sort on student names
*/
sortOrder = NAME;
}
Cursor c = qb.query(db, projection, selection, selectionArgs,null, null, sortOrder);
/**
* register to watch a content URI for changes
*/
c.setNotificationUri(getContext().getContentResolver(), uri);
return c;
}
@Override
public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
int count = 0;
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case STUDENTS:
count = db.delete(STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME, selection, selectionArgs);
break;
case STUDENT_ID:
String id = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
count = db.delete( STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME, _ID + " = " + id +
(!TextUtils.isEmpty(selection) ? " AND (" + selection + ')' : ""), selectionArgs);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI " + uri);
}
getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null);
return count;
}
@Override
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
int count = 0;
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case STUDENTS:
count = db.update(STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME, values, selection, selectionArgs);
break;
case STUDENT_ID:
count = db.update(STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME, values, _ID + " = " + uri.getPathSegments().get(1) +
(!TextUtils.isEmpty(selection) ? " AND (" +selection + ')' : ""), selectionArgs);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI " + uri );
}
getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null);
return count;
}
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
/**
* Get all student records
*/
case STUDENTS:
return "vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.example.students";
/**
* Get a particular student
*/
case STUDENT_ID:
return "vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.example.students";
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported URI: " + uri);
}
}
}
Following will the modified content of AndroidManifest.xml file. Here we have added <provider.../> tag to include our content provider:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.My Application"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="22" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.My Application.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<provider android:name="StudentsProvider"
<android:authorities="com.example.provider.College">
</provider>
</application>
</manifest>
Following will be the content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file to include a button to broadcast your custom intent −<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity"/">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Content provider"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:textSize="30dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tutorials point "
android:textColor="#ff87ff09"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/imageButton"
android:src="@drawable/abc"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:text="Add Name"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/textView2"
android:onClick="onClickAddName"/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/editText"
android:layout_below="@+id/imageButton"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/imageButton"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/imageButton" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_alignTop="@+id/editText"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/textView1"
android:hint="Name"
android:textColorHint="@android:color/holo_blue_light" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/editText2"
android:hint="Grade"
android:textColorHint="@android:color/holo_blue_bright" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Retrive student"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_below="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/button2"
android:onClick="onClickRetrieveStudents"/>
</RelativeLayout>
Make sure you have following content of res/values/strings.xml file:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="app_name">My Application</string>
<string name="action_settings">Settings</string>
</resources>;
Let's try to run our modified My Application application we just created. I assume you had created your AVD
while doing environment set-up. To run the app from Android Studio IDE,
open one of your project's activity files and click Run  icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window, be patience because it may
take sometime based on your computer speed:
icon from the tool bar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your set-up and application,
it will display following Emulator window, be patience because it may
take sometime based on your computer speed: Now let's enter student Name and Grade and finally click on Add Name
button, this will add student record in the database and will flash a
message at the bottom showing ContentProvider URI along with record
number added in the database. This operation makes use of our insert() method. Let's repeat this process to add few more students in the database of our content provider.
Now let's enter student Name and Grade and finally click on Add Name
button, this will add student record in the database and will flash a
message at the bottom showing ContentProvider URI along with record
number added in the database. This operation makes use of our insert() method. Let's repeat this process to add few more students in the database of our content provider. Once you are done with adding records in the database, now its time
to ask ContentProvider to give us those records back, so let's click Retrieve Students button which will fetch and display all the records one by one which is as per our the implementation of our query() method.
Once you are done with adding records in the database, now its time
to ask ContentProvider to give us those records back, so let's click Retrieve Students button which will fetch and display all the records one by one which is as per our the implementation of our query() method.You can write activities against update and delete operations by providing callback functions in MainActivity.java file and then modify user interface to have buttons for update and deleted operations in the same way as we have done for add and read operations.
This way you can use existing Content Provider like Address Book or you can use Content Provider concept in developing nice database oriented applications where you can perform all sort of database operations like read, write, update and delete as explained above in the example.
Android - Fragments
A Fragment is a piece of an activity which enable more modular activity design. It will not be wrong if we say, a fragment is a kind of sub-activity.Following are important points about fragment −
- A fragment has its own layout and its own behaviour with its own life cycle callbacks.
- You can add or remove fragments in an activity while the activity is running.
- You can combine multiple fragments in a single activity to build a multi-plane UI.
- A fragment can be used in multiple activities.
- Fragment life cycle is closely related to the life cycle of its host activity which means when the activity is paused, all the fragments available in the activity will also be stopped.
- A fragment can implement a behaviour that has no user interface component.
- Fragments were added to the Android API in Honeycomb version of Android which API version 11.
Prior to fragment introduction, we had a limitation because we can show only a single activity on the screen at one given point in time. So we were not able to divide device screen and control different parts separately. But with the introduction of fragment we got more flexibility and removed the limitation of having a single activity on the screen at a time. Now we can have a single activity but each activity can comprise of multiple fragments which will have their own layout, events and complete life cycle.
Following is a typical example of how two UI modules defined by fragments can be combined into one activity for a tablet design, but separated for a handset design.
 The application can embed two fragments in Activity A, when running
on a tablet-sized device. However, on a handset-sized screen, there's
not enough room for both fragments, so Activity A includes only the
fragment for the list of articles, and when the user selects an article,
it starts Activity B, which includes the second fragment to read the
article.
The application can embed two fragments in Activity A, when running
on a tablet-sized device. However, on a handset-sized screen, there's
not enough room for both fragments, so Activity A includes only the
fragment for the list of articles, and when the user selects an article,
it starts Activity B, which includes the second fragment to read the
article.Fragment Life Cycle
Android fragments have their own life cycle very similar to an android activity. This section briefs different stages of its life cycle.
Fragment lifecycle
Here is the list of methods which you can to override in your fragment class −- onAttach()The fragment instance is associated with an activity instance.The fragment and the activity is not fully initialized. Typically you get in this method a reference to the activity which uses the fragment for further initialization work.
- onCreate() The system calls this method when creating the fragment. You should initialize essential components of the fragment that you want to retain when the fragment is paused or stopped, then resumed.
- onCreateView() The system calls this callback when it's time for the fragment to draw its user interface for the first time. To draw a UI for your fragment, you must return a View component from this method that is the root of your fragment's layout. You can return null if the fragment does not provide a UI.
- onActivityCreated()The onActivityCreated() is called after the onCreateView() method when the host activity is created. Activity and fragment instance have been created as well as the view hierarchy of the activity. At this point, view can be accessed with the findViewById() method. example. In this method you can instantiate objects which require a Context object
- onStart()The onStart() method is called once the fragment gets visible.
- onResume()Fragment becomes active.
- onPause() The system calls this method as the first indication that the user is leaving the fragment. This is usually where you should commit any changes that should be persisted beyond the current user session.
- onStop()Fragment going to be stopped by calling onStop()
- onDestroyView()Fragment view will destroy after call this method
- onDestroy()onDestroy() called to do final clean up of the fragment's state but Not guaranteed to be called by the Android platform.
How to use Fragments?
This involves number of simple steps to create Fragments.- First of all decide how many fragments you want to use in an activity. For example let's we want to use two fragments to handle landscape and portrait modes of the device.
- Next based on number of fragments, create classes which will extend the Fragment class. The Fragment class has above mentioned callback functions. You can override any of the functions based on your requirements.
- Corresponding to each fragment, you will need to create layout files in XML file. These files will have layout for the defined fragments.
- Finally modify activity file to define the actual logic of replacing fragments based on your requirement.
Types of Fragments
Basically fragments are divided as three stages as shown below.- Single frame fragments − Single frame fragments are using for hand hold devices like mobiles, here we can show only one fragment as a view.
- List fragments − fragments having special list view is called as list fragment
- Fragments transaction − Using with fragment transaction. we can move one fragment to another fragment.
Android - Intents and Filters
An Android Intent is an abstract description of an operation to be performed. It can be used with startActivity to launch an Activity, broadcastIntent to send it to any interested BroadcastReceiver components, and startService(Intent) or bindService(Intent, ServiceConnection, int) to communicate with a background Service.
The intent itself, an Intent object, is a passive data structure holding an abstract description of an operation to be performed.
For example, let's assume that you have an Activity that needs to launch an email client and sends an email using your Android device. For this purpose, your Activity would send an ACTION_SEND along with appropriate chooser, to the Android Intent Resolver. The specified chooser gives the proper interface for the user to pick how to send your email data.
Intent email = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND, Uri.parse("mailto:")); email.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_EMAIL, recipients); email.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SUBJECT, subject.getText().toString()); email.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TEXT, body.getText().toString()); startActivity(Intent.createChooser(email, "Choose an email client from..."));
Above syntax is calling startActivity method to start an email activity and result should be as shown below
 For example, assume that you have an Activity that needs to open URL
in a web browser on your Android device. For this purpose, your Activity
will send ACTION_WEB_SEARCH Intent to the Android Intent Resolver to
open given URL in the web browser. The Intent Resolver parses through a
list of Activities and chooses the one that would best match your
Intent, in this case, the Web Browser Activity. The Intent Resolver then
passes your web page to the web browser and starts the Web Browser
Activity.
For example, assume that you have an Activity that needs to open URL
in a web browser on your Android device. For this purpose, your Activity
will send ACTION_WEB_SEARCH Intent to the Android Intent Resolver to
open given URL in the web browser. The Intent Resolver parses through a
list of Activities and chooses the one that would best match your
Intent, in this case, the Web Browser Activity. The Intent Resolver then
passes your web page to the web browser and starts the Web Browser
Activity.
String q = "tutorialspoint"; Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_WEB_SEARCH ); intent.putExtra(SearchManager.QUERY, q); startActivity(intent);
Above example will search as tutorialspoint on android search engine and it gives the result of tutorialspoint in your an activity
There are separate mechanisms for delivering intents to each type of component - activities, services, and broadcast receivers.
Sr.No Method & Description 1 Context.startActivity() The Intent object is passed to this method to launch a new activity or get an existing activity to do something new. 2 Context.startService() The Intent object is passed to this method to initiate a service or deliver new instructions to an ongoing service. 3 Context.sendBroadcast() The Intent object is passed to this method to deliver the message to all interested broadcast receivers. Intent Objects
An Intent object is a bundle of information which is used by the component that receives the intent as well as information used by the Android system.
An Intent object can contain the following components based on what it is communicating or going to perform −
Action
This is mandatory part of the Intent object and is a string naming the action to be performed — or, in the case of broadcast intents, the action that took place and is being reported. The action largely determines how the rest of the intent object is structured . The Intent class defines a number of action constants corresponding to different intents. Here is a list of Android Intent Standard Actions
The action in an Intent object can be set by the setAction() method and read by getAction().
Data
Adds a data specification to an intent filter. The specification can be just a data type (the mimeType attribute), just a URI, or both a data type and a URI. A URI is specified by separate attributes for each of its parts −
These attributes that specify the URL format are optional, but also mutually dependent −
- If a scheme is not specified for the intent filter, all the other URI attributes are ignored.
- If a host is not specified for the filter, the port attribute and all the path attributes are ignored.
Some examples of action/data pairs are −
| S.N. | Action/Data Pair & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | ACTION_VIEW content://contacts/people/1 Display information about the person whose identifier is "1". |
| 2 | ACTION_DIAL content://contacts/people/1 Display the phone dialer with the person filled in. |
| 3 | ACTION_VIEW tel:123 Display the phone dialer with the given number filled in. |
| 4 | ACTION_DIAL tel:123 Display the phone dialer with the given number filled in. |
| 5 | ACTION_EDIT content://contacts/people/1 Edit information about the person whose identifier is "1". |
| 6 | ACTION_VIEW content://contacts/people/ Display a list of people, which the user can browse through. |
| 7 | ACTION_SET_WALLPAPER Show settings for choosing wallpaper |
| 8 | ACTION_SYNC It going to be synchronous the data,Constant Value is android.intent.action.SYNC |
| 9 | ACTION_SYSTEM_TUTORIAL It will start the platform-defined tutorial(Default tutorial or start up tutorial) |
| 10 | ACTION_TIMEZONE_CHANGED It intimates when time zone has changed |
| 11 | ACTION_UNINSTALL_PACKAGE It is used to run default uninstaller |
Category
The category is an optional part of Intent object and it's a string containing additional information about the kind of component that should handle the intent. The addCategory() method places a category in an Intent object, removeCategory() deletes a category previously added, and getCategories() gets the set of all categories currently in the object. Here is a list of Android Intent Standard Categories.You can check detail on Intent Filters in below section to understand how do we use categories to choose appropriate activity corresponding to an Intent.
Extras
This will be in key-value pairs for additional information that should be delivered to the component handling the intent. The extras can be set and read using the putExtras() and getExtras() methods respectively. Here is a list of Android Intent Standard Extra DataFlags
These flags are optional part of Intent object and instruct the Android system how to launch an activity, and how to treat it after it's launched etc.| Sr.No | Flags & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK If set in an Intent passed to Context.startActivity(), this flag will cause any existing task that would be associated with the activity to be cleared before the activity is started. That is, the activity becomes the new root of an otherwise empty task, and any old activities are finished. This can only be used in conjunction with FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK. |
| 2 | FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP If set, and the activity being launched is already running in the current task, then instead of launching a new instance of that activity, all of the other activities on top of it will be closed and this Intent will be delivered to the (now on top) old activity as a new Intent. |
| 3 | FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK This flag is generally used by activities that want to present a "launcher" style behavior: they give the user a list of separate things that can be done, which otherwise run completely independently of the activity launching them. |
Component Name
This optional field is an android ComponentName object representing either Activity, Service or BroadcastReceiver class. If it is set, the Intent object is delivered to an instance of the designated class otherwise Android uses other information in the Intent object to locate a suitable target.The component name is set by setComponent(), setClass(), or setClassName() and read by getComponent().
Types of Intents
There are following two types of intents supported by Android
Explicit Intents
Explicit intent going to be connected internal world of application,suppose if you wants to connect one activity to another activity, we can do this quote by explicit intent, below image is connecting first activity to second activity by clicking button. These intents designate the target component by its name and they are
typically used for application-internal messages - such as an activity
starting a subordinate service or launching a sister activity. For
example −
These intents designate the target component by its name and they are
typically used for application-internal messages - such as an activity
starting a subordinate service or launching a sister activity. For
example −// Explicit Intent by specifying its class name Intent i = new Intent(FirstActivity.this, SecondActivity.class); // Starts TargetActivity startActivity(i);
Implicit Intents
These intents do not name a target and the field for the component name is left blank. Implicit intents are often used to activate components in other applications. For example −Intent read1=new Intent(); read1.setAction(android.content.Intent.ACTION_VIEW); read1.setData(ContactsContract.Contacts.CONTENT_URI); startActivity(read1);Above code will give result as shown below
 The target component which receives the intent can use the getExtras() method to get the extra data sent by the source component. For example −
The target component which receives the intent can use the getExtras() method to get the extra data sent by the source component. For example −// Get bundle object at appropriate place in your code Bundle extras = getIntent().getExtras(); // Extract data using passed keys String value1 = extras.getString("Key1"); String value2 = extras.getString("Key2");
Example
Following example shows the functionality of a Android Intent to launch various Android built-in applications.| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | You will use Android studio IDE to create an Android application and name it as My Application under a package com.example.saira_000.myapplication. While creating this project, make sure you Target SDK and Compile With at the latest version of Android SDK to use higher levels of APIs. |
| 2 | Modify src/main/java/MainActivity.java file and add the code to define two listeners corresponding two buttons ie. Start Browser and Start Phone. |
| 3 | Modify layout XML file res/layout/activity_main.xml to add three buttons in linear layout. |
| 4 | Run the application to launch Android emulator and verify the result of the changes done in the application. |
package com.example.saira_000.myapplication; import android.content.Intent; import android.net.Uri; import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuItem; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity { Button b1,b2; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); b1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button); b1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent i = new Intent(android.content.Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse("http://www.example.com")); startActivity(i); } }); b2=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button2); b2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent i = new Intent(android.content.Intent.ACTION_VIEW,Uri.parse("tel:9510300000")); startActivity(i); } }); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu); return true; } @Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { // Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will // automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long // as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml. int id = item.getItemId(); //noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement if (id == R.id.action_settings) { return true; } return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); } }Following will be the content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file −
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Intent Example" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:textSize="30dp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Tutorials point" android:textColor="#ff87ff09" android:textSize="30dp" android:layout_below="@+id/textView1" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <ImageButton android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/imageButton" android:src="@drawable/abc" android:layout_below="@+id/textView2" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <EditText android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/editText" android:layout_below="@+id/imageButton" android:layout_alignRight="@+id/imageButton" android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/imageButton" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Start Browser" android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_alignTop="@+id/editText" android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView1" android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/textView1" android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/imageButton" android:layout_alignStart="@+id/imageButton" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Start Phone" android:id="@+id/button2" android:layout_below="@+id/button" android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button" android:layout_alignStart="@+id/button" android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView2" android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/textView2" /> </RelativeLayout>Following will be the content of res/values/strings.xml to define two new constants −
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="app_name">My Applicaiton</string> <string name="action_settings">Settings</string> </resources>Following is the default content of AndroidManifest.xml −
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.My Application" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="22" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name="com.example.saira_000.myapplication.MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>Let's try to run your My Application application. I assume you had created your AVD while doing environment setup. To run the app from Android Studio, open one of your project's activity files and click Run
 icon from the toolbar.Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it
will display following Emulator window −
icon from the toolbar.Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it
will display following Emulator window − Now click on Start Browser button, which will start a browser configured and display http://www.example.com as shown below −
Now click on Start Browser button, which will start a browser configured and display http://www.example.com as shown below − Similar way you can launch phone interface using Start Phone button, which will allow you to dial already given phone number.
Similar way you can launch phone interface using Start Phone button, which will allow you to dial already given phone number.Intent Filters
You have seen how an Intent has been used to call an another activity. Android OS uses filters to pinpoint the set of Activities, Services, and Broadcast receivers that can handle the Intent with help of specified set of action, categories, data scheme associated with an Intent. You will use <intent-filter> element in the manifest file to list down actions, categories and data types associated with any activity, service, or broadcast receiver.Following is an example of a part of AndroidManifest.xml file to specify an activity com.example.My Application.CustomActivity which can be invoked by either of the two mentioned actions, one category, and one data −
<activity android:name=".CustomActivity" android:label="@string/app_name"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <action android:name="com.example.My Application.LAUNCH" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <data android:scheme="http" /> </intent-filter> </activity>Once this activity is defined along with above mentioned filters, other activities will be able to invoke this activity using either the android.intent.action.VIEW, or using the com.example.My Application.LAUNCH action provided their category is android.intent.category.DEFAULT.
The <data> element specifies the data type expected by the activity to be called and for above example our custom activity expects the data to start with the "http://"
There may be a situation that an intent can pass through the filters of more than one activity or service, the user may be asked which component to activate. An exception is raised if no target can be found.
There are following test Android checks before invoking an activity −
- A filter <intent-filter> may list more than one action as shown above but this list cannot be empty; a filter must contain at least one <action> element, otherwise it will block all intents. If more than one actions are mentioned then Android tries to match one of the mentioned actions before invoking the activity.
- A filter <intent-filter> may list zero, one or more than one categories. if there is no category mentioned then Android always pass this test but if more than one categories are mentioned then for an intent to pass the category test, every category in the Intent object must match a category in the filter.
- Each <data> element can specify a URI and a data type (MIME media type). There are separate attributes like scheme, host, port, and path for each part of the URI. An Intent object that contains both a URI and a data type passes the data type part of the test only if its type matches a type listed in the filter.
Example
Following example is a modification of the above example. Here we will see how Android resolves conflict if one intent is invoking two activities defined in , next how to invoke a custom activity using a filter and third one is an exception case if Android does not file appropriate activity defined for an intent.| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | You will use android studio to create an Android application and name it as My Application under a package com.example.saira_000.myapplication. While creating this project, make sure you Target SDK and Compile With at the latest version of Android SDK to use higher levels of APIs. |
| 2 | Modify src/Main/Java/MainActivity.java file and add the code to define three listeners corresponding to three buttons defined in layout file. |
| 3 | Add a new src/Main/Java/CustomActivity.java file to have one custom activity which will be invoked by different intents. |
| 4 | Modify layout XML file res/layout/activity_main.xml to add three buttons in linear layout. |
| 5 | Add one layout XML file res/layout/custom_view.xml to add a simple <TextView> to show the passed data through intent. |
| 6 | Modify AndroidManifest.xml to add <intent-filter> to define rules for your intent to invoke custom activity. |
| 7 | Run the application to launch Android emulator and verify the result of the changes done in the application. |
package com.example.saira_000.myapplication; import android.content.Intent; import android.net.Uri; import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuItem; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity { Button b1,b2,b3; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); b1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button); b1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent i = new Intent(android.content.Intent.ACTION_VIEW,Uri.parse("http://www.example.com")); startActivity(i); } }); b2=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button2); b2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent i = new Intent("com.example.My Application.LAUNCH",Uri.parse("http://www.example.com")); startActivity(i); } }); b3=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button3); b3.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent i = new Intent("com.example.My Application.LAUNCH",Uri.parse("https://www.example.com")); startActivity(i); } }); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu); return true; } @Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { // Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will // automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long // as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml. int id = item.getItemId(); //noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement if (id == R.id.action_settings) { return true; } return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); } }Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/com.example.My Application/CustomActivity.java.
package com.example.saira_000.myapplication; import android.app.Activity; import android.net.Uri; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.TextView; public class CustomActivity extends Activity { @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.custom_view); TextView label = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.show_data); Uri url = getIntent().getData(); label.setText(url.toString()); } }Following will be the content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file −
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Intent Example" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:textSize="30dp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Tutorials point" android:textColor="#ff87ff09" android:textSize="30dp" android:layout_below="@+id/textView1" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <ImageButton android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/imageButton" android:src="@drawable/abc" android:layout_below="@+id/textView2" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <EditText android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/editText" android:layout_below="@+id/imageButton" android:layout_alignRight="@+id/imageButton" android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/imageButton" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Start browsing with view action" android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_alignTop="@+id/editText" android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView1" android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/textView1" android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/imageButton" android:layout_alignStart="@+id/imageButton" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Start browsing with launch action" android:id="@+id/button2" android:layout_below="@+id/button" android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button" android:layout_alignStart="@+id/button" android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView2" android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/textView2" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Exceptional condition" android:id="@+id/button3" android:layout_below="@+id/button2" android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button2" android:layout_alignStart="@+id/button2" android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView2" android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/textView2" /> </RelativeLayout>Following will be the content of res/layout/custom_view.xml file −
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/show_data" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="400dp"/> </LinearLayout>Following will be the content of res/values/strings.xml to define two new constants −
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="app_name">My Application</string> <string name="action_settings">Settings</string> </resources>Following is the default content of AndroidManifest.xml −
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.My Application" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="22" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name="com.example.saira_000.myapplication" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name="com.example.saira_000.myapplication.CustomActivity" <android:label="@string/app_name"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <action android:name="com.example.saira_000.myapplication.LAUNCH" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <data android:scheme="http" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>Let's try to run your My Application application. I assume you had created your AVD while doing environment setup. To run the app from Android Studio, open one of your project's activity files and click Run
 icon from the toolbar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it
will display following Emulator window −
icon from the toolbar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and
starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it
will display following Emulator window − Now let's start with first button "Start Browser with VIEW Action".
Here we have defined our custom activity with a filter
"android.intent.action.VIEW", and there is already one default activity
against VIEW action defined by Android which is launching web browser,
So android displays following two options to select the activity you
want to launch.
Now let's start with first button "Start Browser with VIEW Action".
Here we have defined our custom activity with a filter
"android.intent.action.VIEW", and there is already one default activity
against VIEW action defined by Android which is launching web browser,
So android displays following two options to select the activity you
want to launch. Now if you select Browser, then Android will launch web browser and
open example.com website but if you select IndentDemo option then
Android will launch CustomActivity which does nothing but just capture
passed data and displays in a text view as follows −
Now if you select Browser, then Android will launch web browser and
open example.com website but if you select IndentDemo option then
Android will launch CustomActivity which does nothing but just capture
passed data and displays in a text view as follows − Now go back using back button and click on "Start Browser with LAUNCH
Action" button, here Android applies filter to choose define activity
and it simply launch your custom activity
Now go back using back button and click on "Start Browser with LAUNCH
Action" button, here Android applies filter to choose define activity
and it simply launch your custom activityAgain, go back using back button and click on "Exception Condition" button, here Android tries to find out a valid filter for the given intent but it does not find a valid activity defined because this time we have used data as https instead of http though we are giving a correct action, so Android raises an exception and shows following screen −
Android - UI Layouts
The basic building block for user interface is a View object which is created from the View class and occupies a rectangular area on the screen and is responsible for drawing and event handling. View is the base class for widgets, which are used to create interactive UI components like buttons, text fields, etc.The ViewGroup is a subclass of View and provides invisible container that hold other Views or other ViewGroups and define their layout properties.
At third level we have different layouts which are subclasses of ViewGroup class and a typical layout defines the visual structure for an Android user interface and can be created either at run time using View/ViewGroup objects or you can declare your layout using simple XML file main_layout.xml which is located in the res/layout folder of your project.

Layout params
This tutorial is more about creating your GUI based on layouts defined in XML file. A layout may contain any type of widgets such as buttons, labels, textboxes, and so on. Following is a simple example of XML file having LinearLayout:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is a TextView" />
<Button android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is a Button" />
<!-- More GUI components go here -->
</LinearLayout>
Once your layout has created, you can load the layout resource from your application code, in your Activity.onCreate() callback implementation as shown below −public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
Android Layout Types
There are number of Layouts provided by Android which you will use in almost all the Android applications to provide different view, look and feel.| Sr.No | Layout & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Linear Layout LinearLayout is a view group that aligns all children in a single direction, vertically or horizontally. |
| 2 | Relative Layout RelativeLayout is a view group that displays child views in relative positions. |
| 3 | Table Layout TableLayout is a view that groups views into rows and columns. |
| 4 | Absolute Layout AbsoluteLayout enables you to specify the exact location of its children. |
| 5 | Frame Layout The FrameLayout is a placeholder on screen that you can use to display a single view. |
| 6 | List View ListView is a view group that displays a list of scrollable items. |
| 7 | Grid View GridView is a ViewGroup that displays items in a two-dimensional, scrollable grid. |
Layout Attributes
Each layout has a set of attributes which define the visual properties of that layout. There are few common attributes among all the layouts and their are other attributes which are specific to that layout. Following are common attributes and will be applied to all the layouts:| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| android:id | This is the ID which uniquely identifies the view. |
| android:layout_width | This is the width of the layout. |
| android:layout_height | This is the height of the layout |
| android:layout_marginTop | This is the extra space on the top side of the layout. |
| android:layout_marginBottom | This is the extra space on the bottom side of the layout. |
| android:layout_marginLeft | This is the extra space on the left side of the layout. |
| android:layout_marginRight | This is the extra space on the right side of the layout. |
| android:layout_gravity | This specifies how child Views are positioned. |
| android:layout_weight | This specifies how much of the extra space in the layout should be allocated to the View. |
| android:layout_x | This specifies the x-coordinate of the layout. |
| android:layout_y | This specifies the y-coordinate of the layout. |
| android:layout_width | This is the width of the layout. |
| android:layout_width | This is the width of the layout. |
| android:paddingLeft | This is the left padding filled for the layout. |
| android:paddingRight | This is the right padding filled for the layout. |
| android:paddingTop | This is the top padding filled for the layout. |
| android:paddingBottom | This is the bottom padding filled for the layout. |
You can specify width and height with exact measurements but more often, you will use one of these constants to set the width or height −
- android:layout_width=wrap_content tells your view to size itself to the dimensions required by its content.
- android:layout_width=fill_parent tells your view to become as big as its parent view.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| top | 0x30 | Push object to the top of its container, not changing its size. |
| bottom | 0x50 | Push object to the bottom of its container, not changing its size. |
| left | 0x03 | Push object to the left of its container, not changing its size. |
| right | 0x05 | Push object to the right of its container, not changing its size. |
| center_vertical | 0x10 | Place object in the vertical center of its container, not changing its size. |
| fill_vertical | 0x70 | Grow the vertical size of the object if needed so it completely fills its container. |
| center_horizontal | 0x01 | Place object in the horizontal center of its container, not changing its size. |
| fill_horizontal | 0x07 | Grow the horizontal size of the object if needed so it completely fills its container. |
| center | 0x11 | Place the object in the center of its container in both the vertical and horizontal axis, not changing its size. |
| fill | 0x77 | Grow the horizontal and vertical size of the object if needed so it completely fills its container. |
| clip_vertical | 0x80 | Additional option that can be set to have the top and/or bottom edges of the child clipped to its container's bounds. The clip will be based on the vertical gravity: a top gravity will clip the bottom edge, a bottom gravity will clip the top edge, and neither will clip both edges. |
| clip_horizontal | 0x08 | Additional option that can be set to have the left and/or right edges of the child clipped to its container's bounds. The clip will be based on the horizontal gravity: a left gravity will clip the right edge, a right gravity will clip the left edge, and neither will clip both edges. |
| start | 0x00800003 | Push object to the beginning of its container, not changing its size. |
| end | 0x00800005 | Push object to the end of its container, not changing its size. |
View Identification
A view object may have a unique ID assigned to it which will identify the View uniquely within the tree. The syntax for an ID, inside an XML tag is −android:id="@+id/my_button"Following is a brief description of @ and + signs −
- The at-symbol (@) at the beginning of the string indicates that the XML parser should parse and expand the rest of the ID string and identify it as an ID resource.
- The plus-symbol (+) means that this is a new resource name that
must be created and added to our resources. To create an instance of the
view object and capture it from the layout, use the following −
Button myButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.my_button);
Android - UI Controls
Input controls are the interactive components in your app's user interface. Android provides a wide variety of controls you can use in your UI, such as buttons, text fields, seek bars, check box, zoom buttons, toggle buttons, and many more.

UI Elements
A View is an object that draws something on the screen that the user can interact with and a ViewGroup is an object that holds other View (and ViewGroup) objects in order to define the layout of the user interface.You define your layout in an XML file which offers a human-readable structure for the layout, similar to HTML. For example, a simple vertical layout with a text view and a button looks like this −
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="I am a TextView" />
<Button android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="I am a Button" />
</LinearLayout>
Android UI Controls
There are number of UI controls provided by Android that allow you to build the graphical user interface for your app.| S.N. | UI Control & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | TextView This control is used to display text to the user. |
| 2 | EditText EditText is a predefined subclass of TextView that includes rich editing capabilities. |
| 3 | AutoCompleteTextView The AutoCompleteTextView is a view that is similar to EditText, except that it shows a list of completion suggestions automatically while the user is typing. |
| 4 | Button A push-button that can be pressed, or clicked, by the user to perform an action. |
| 5 | ImageButton AbsoluteLayout enables you to specify the exact location of its children. |
| 6 | CheckBox An on/off switch that can be toggled by the user. You should use check box when presenting users with a group of selectable options that are not mutually exclusive. |
| 7 | ToggleButton An on/off button with a light indicator. |
| 8 | RadioButton The RadioButton has two states: either checked or unchecked. |
| 9 | RadioGroup A RadioGroup is used to group together one or more RadioButtons. |
| 10 | ProgressBar The ProgressBar view provides visual feedback about some ongoing tasks, such as when you are performing a task in the background. |
| 11 | Spinner A drop-down list that allows users to select one value from a set. |
| 12 | TimePicker The TimePicker view enables users to select a time of the day, in either 24-hour mode or AM/PM mode. |
| 13 | DatePicker The DatePicker view enables users to select a date of the day. |
Create UI Controls
Input controls are the interactive components in your app's user interface. Android provides a wide variety of controls you can use in your UI, such as buttons, text fields, seek bars, check box, zoom buttons, toggle buttons, and many more.As explained in previous chapter, a view object may have a unique ID assigned to it which will identify the View uniquely within the tree. The syntax for an ID, inside an XML tag is −
android:id="@+id/text_id"To create a UI Control/View/Widget you will have to define a view/widget in the layout file and assign it a unique ID as follows −
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView android:id="@+id/text_id"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="I am a TextView" />
</LinearLayout>
Then finally create an instance of the Control object and capture it from the layout, use the following −TextView myText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_id);